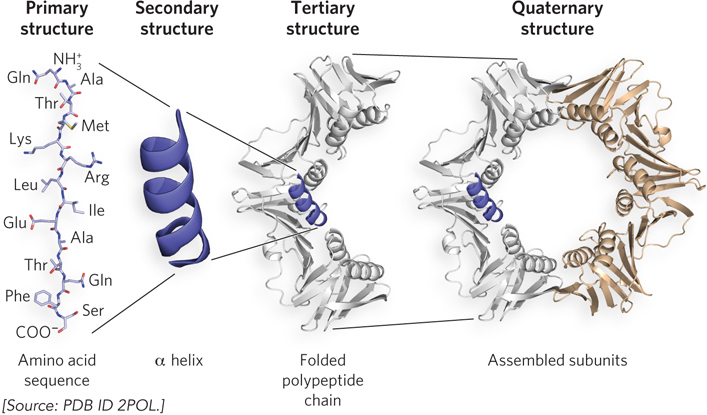
Levels of structure in proteins. The primary structure consists of a sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. The resulting linear polypeptide can be coiled into units of secondary structure, such as an α helix. The helix and other secondary structural elements fold together and define the polypeptide’s tertiary structure. The folded polypeptide shown here is one of the subunits that make up the quaternary structure of a multisubunit protein (composed of more than one polypeptide), the dimeric Escherichia coli β processivity factor, which is involved in DNA replication.