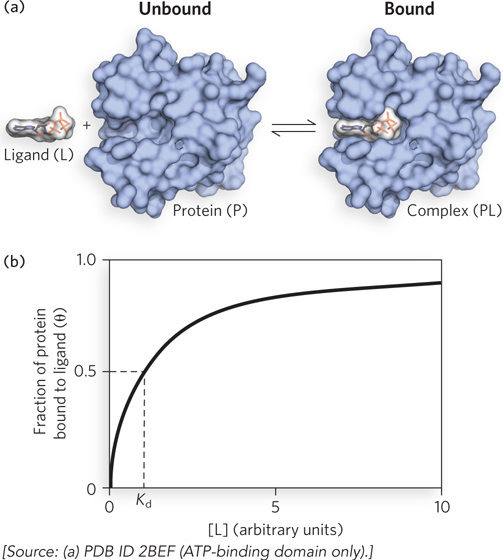
Ligand binding. (a) Reversible binding of a protein (P) to a ligand (L). The protein shown here is nucleoside diphosphate kinase and the ligand is ATP. (b) The fraction of ligand- d-