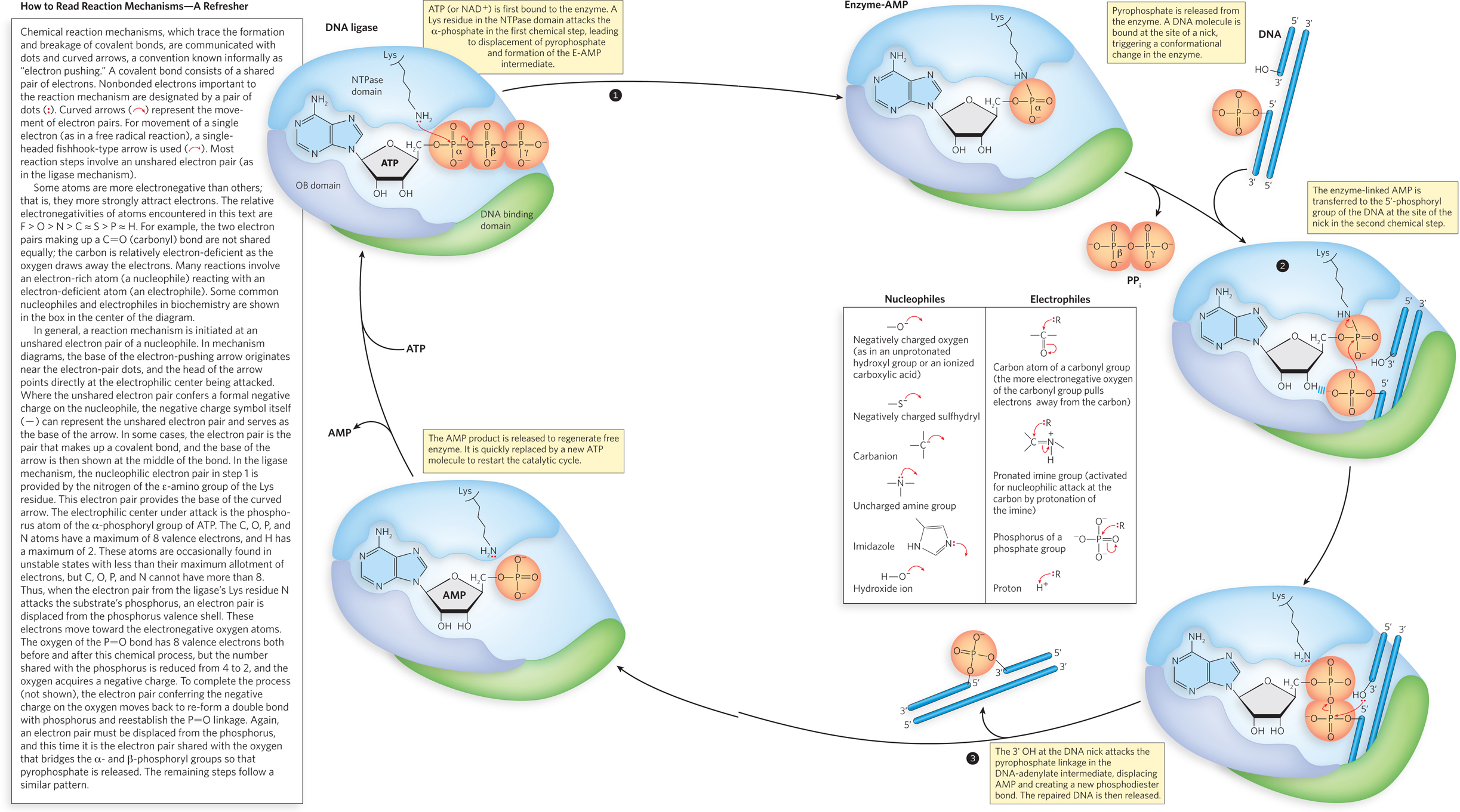
The DNA ligase reaction. The reaction creates a new phosphodiester bond at the site of a break, or nick, in the DNA. The same series of three chemical steps is used by every RNA or DNA ligase. In each of the three steps, one phosphodiester bond is formed at the expense of another. Steps 1 and 2 lead to activation of the 5′ phosphate in the nick. In the E. coli DNA ligase reaction, AMP is derived from NAD+ rather than ATP, and the reaction releases nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) rather than pyrophosphate.