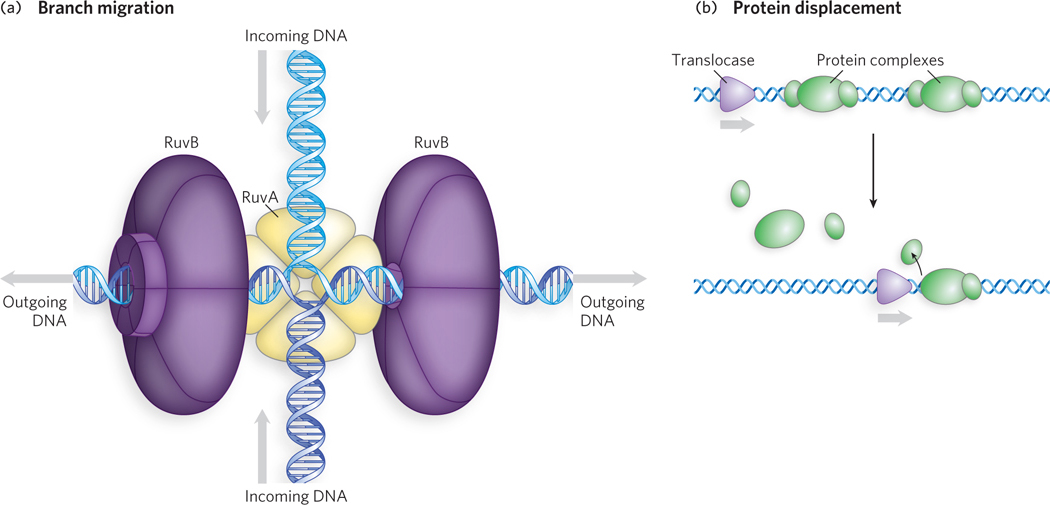
DNA translocases. (a) Branch migration during double- r-