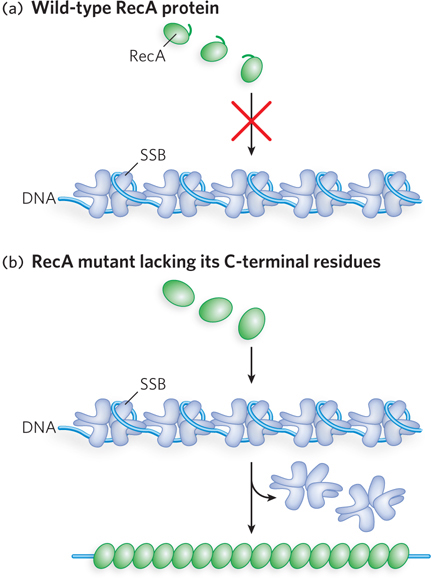
Autoinhibition. (a) The RecA recombinase (see Chapter 13) forms filaments on DNA, characterized by distinct nucleation and filament extension phases. In the bacterial RecA protein, a C- e- e- A– C-