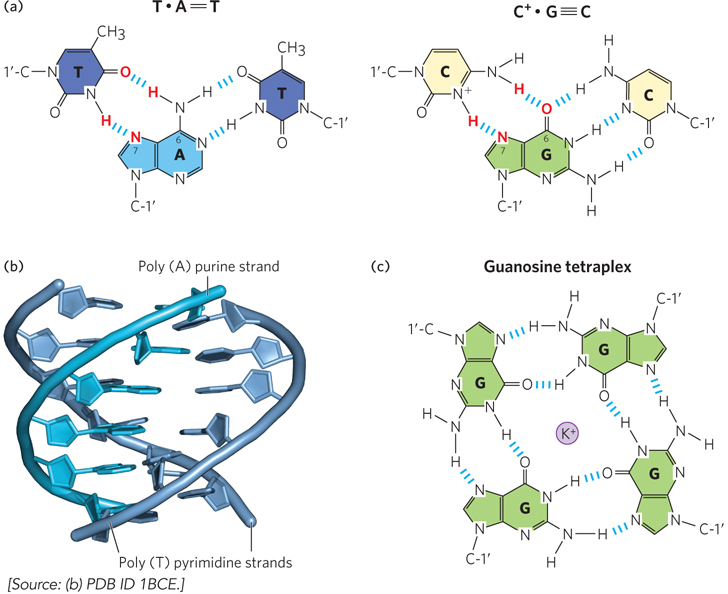
Three- r- n- e- n-