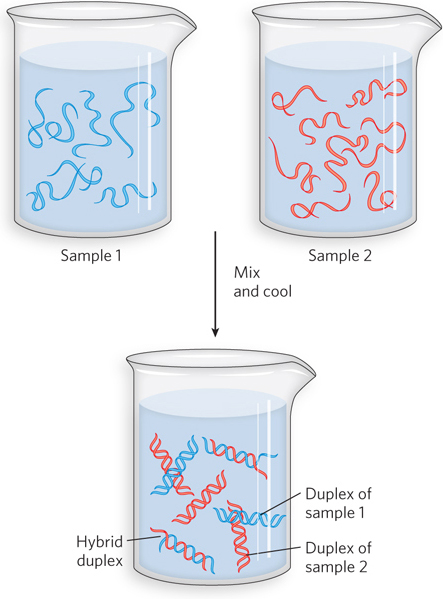
Cross-