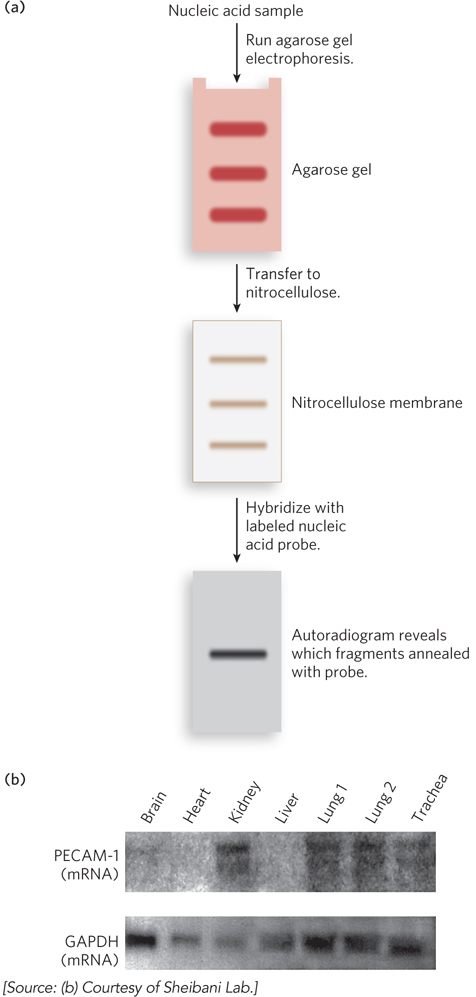
Gel electrophoresis used in the Southern and Northern blotting techniques. (a) Gel electrophoresis is used to size- e- e- P- e— M- 3- M- M-