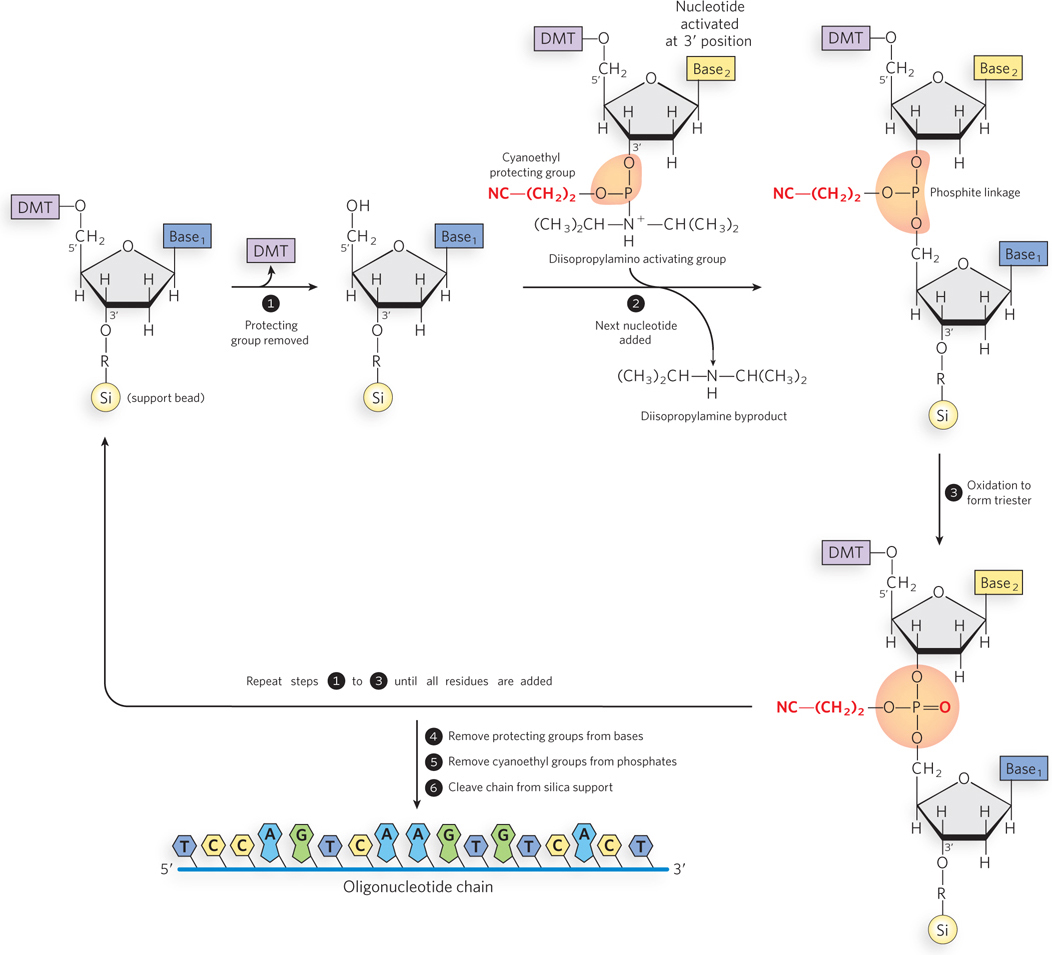
Solid-