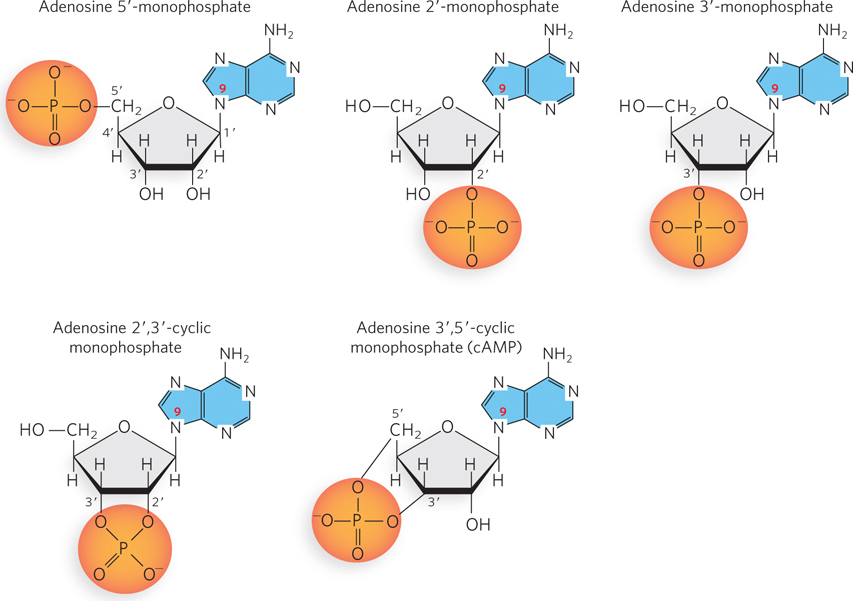
Examples of adenosine monophosphates. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate, with a phosphate group on C- e- 6-