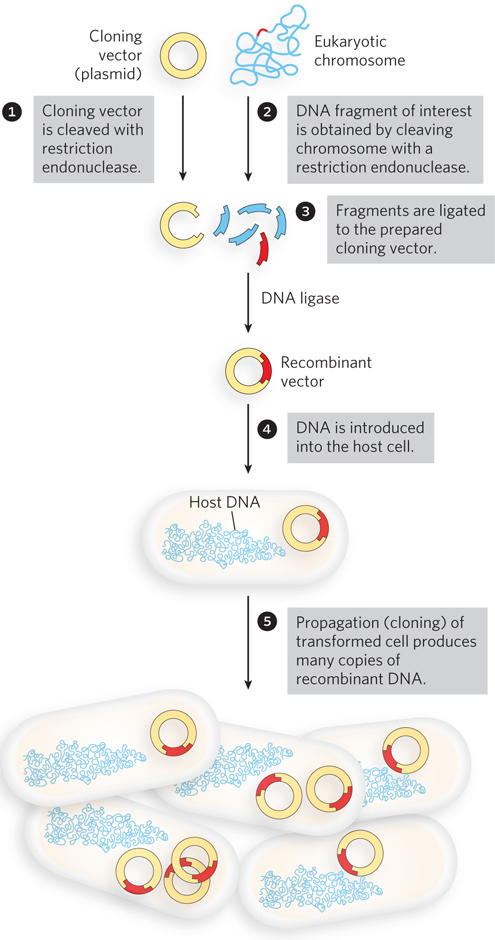
DNA cloning. The process involves cutting two DNAs with restriction enzymes, joining (ligating) the fragments together with DNA ligase, and using the recombinant DNA products to transform a suitable host cell. (This drawing is not to scale; the size of the E. coli chromosome relative to that of a typical cloning vector (such as a plasmid) is much greater than depicted here.)