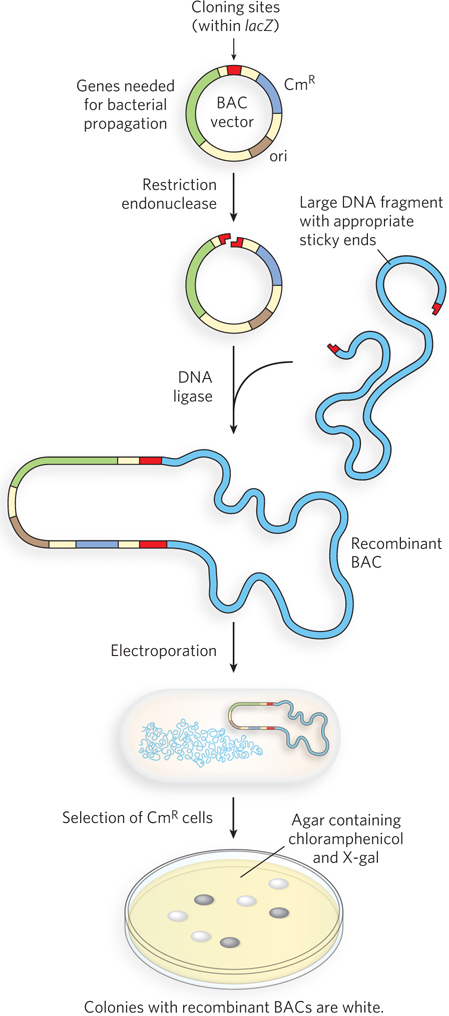
Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) as cloning vectors. After treatment with an appropriate restriction endonuclease, a BAC and a long fragment of DNA are ligated. The recombinant BAC is transferred into E. coli by electroporation, and colonies with recombinant BACs are selected by growth on media containing both the antibiotic chloramphenicol and X-