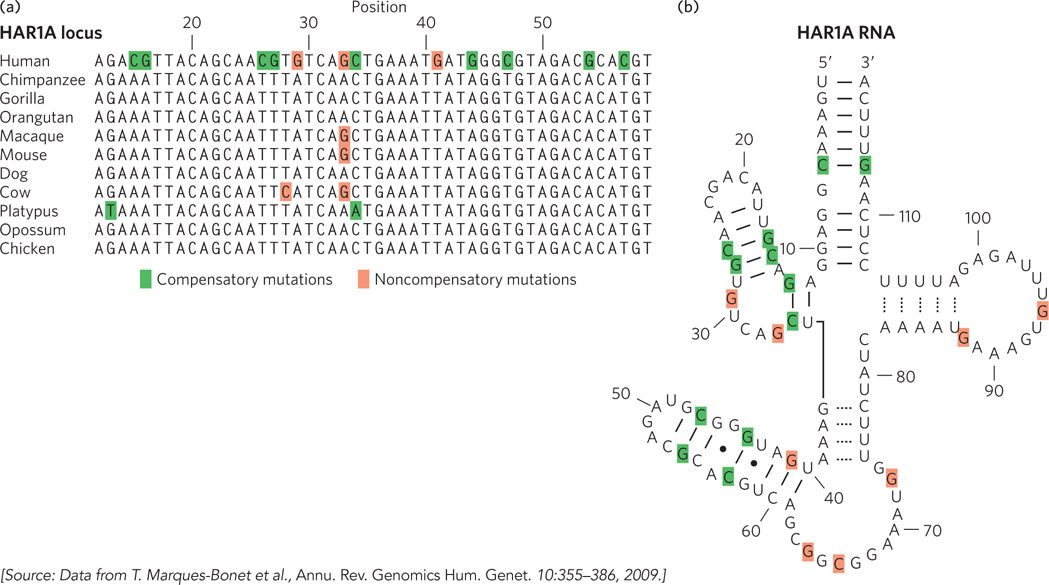
Accelerated evolution in some human genes.(a) The HAR1A locus specifies a noncoding RNA that is highly conserved in vertebrates. This RNA functions in the brain during neurodevelopment. In humans, the HAR1A gene exhibits an unusual number of substitutions (highlighted by color shading), providing evidence of accelerated evolution. (b) The secondary structure of the HAR1A RNA has several paired loops. Many of the sequence changes, shaded green here and in (a), are compensatory in the context of this RNA secondary structure: a change on one side of the loop is mirrored by a compensatory change on the other side of the loop, to permit proper base pairing. Noncompensatory changes are shaded red.