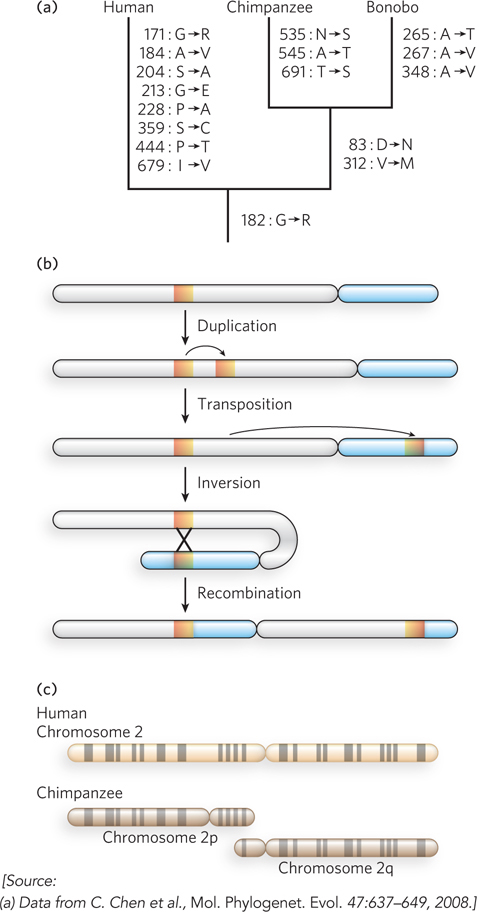
Genomic alterations in the human lineage.(a) This evolutionary tree is for the progesterone receptor, which helps regulate many events in reproduction. The gene encoding this protein has undergone more evolutionary alterations than most. Amino acid changes associated uniquely with humans, chimpanzees, and bonobos are listed beside each branch (with the residue number). (b) One of the multistep processes that can lead to the inversion of a chromosome segment. A gene or segment of the chromosome is duplicated, then moved to another chromosomal location by transposition. Recombination of the two segments may result in inversion of the chromosomal DNA between them. (c) The genes on chimpanzee chromosomes 2p and 2q are homologous to those on human chromosome 2, implying that two chromosomes fused at some point in the line leading to humans. Homologous regions can be visualized by bands created in metaphase chromosomes by certain dyes, as shown here.