DATA ANALYSIS PROBLEM
Olivera, B.M., and I.R. Lehman. 1967. Linkage of polynucleotides through phosphodiester bonds by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 57:1426–
Question 11.16
The discovery of DNA ligase provides some classic examples of the development of enzyme assays (see this chapter’s Moment of Discovery). In the paper first reporting their detection of a DNA-
In their experiments, Olivera and Lehman found that the poly(dT) strands were linked together, because the label became resistant to the alkaline phosphatase treatment. Some of their results are shown below, for a reaction containing 1 μmol (micromole) of labeled DNA ends.
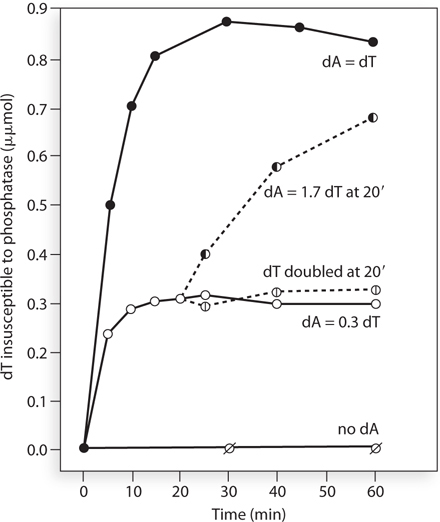
411
Why does the linking reaction make the label resistant to alkaline phosphatase treatment?
The reaction required the addition of poly(dA) in addition to the labeled poly(dT) strands. Suggest a reason.
In one experiment, the investigators added only enough poly(dA) to allow linking of 30% of the poly(dT). After 20 minutes, they added either more poly(dA) or more unlabeled poly(dT). The reaction recommenced only in response to the poly(dA). What does this reveal about the enzyme activity?
A cofactor in the crude extract was needed for the reaction, but it could not be replaced by added ATP. Suggest a reason.