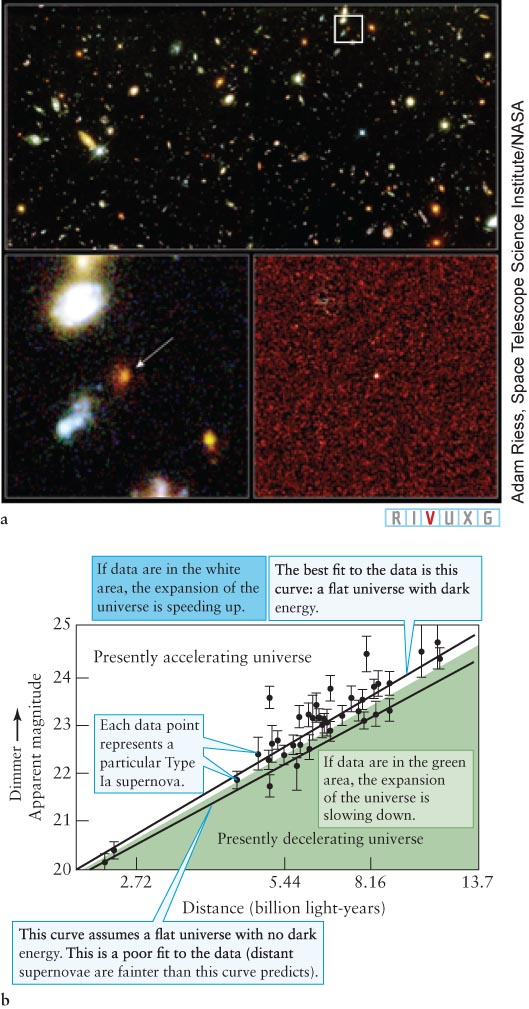
Figure 14- t-