Chapter 1. Psychoactive Drugs
Learning Objectives
Identify the three major categories, or types, of psychoactive drugs.
Contrast the effects of the three major types of psychoactive drugs.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
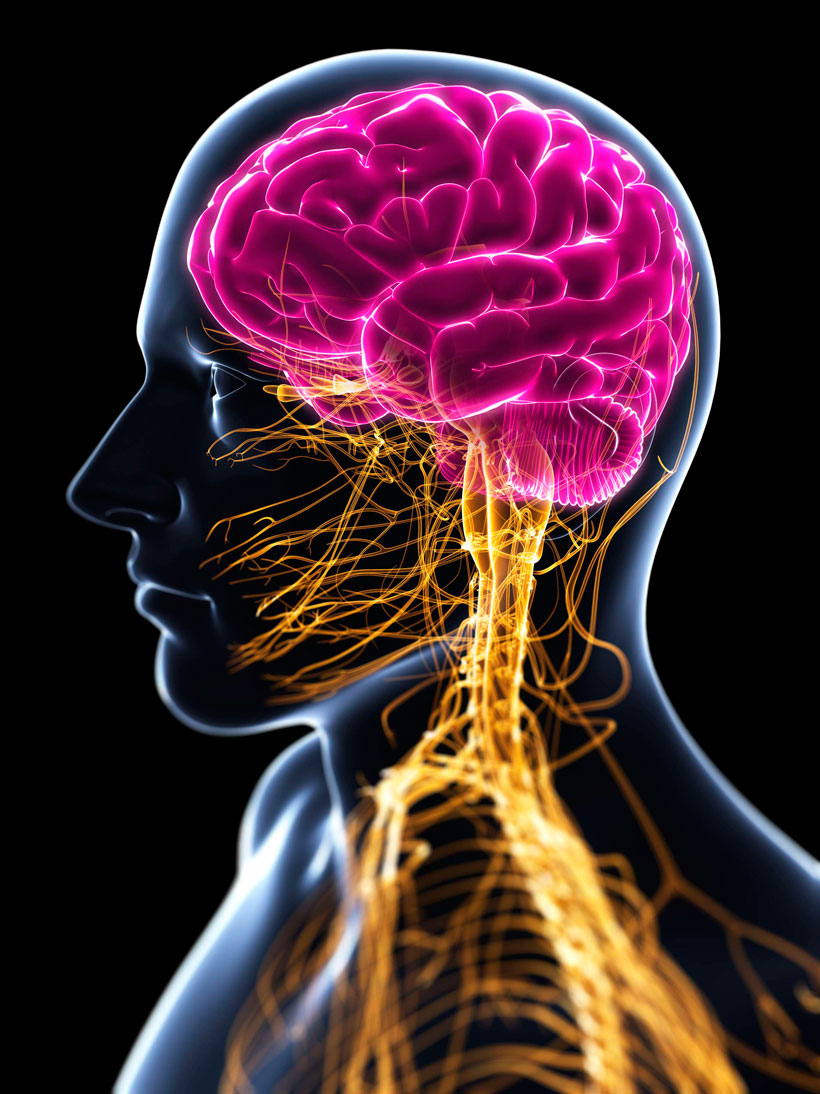
1. Psychoactive drugs alter the functioning of the brain by enhancing or inhibiting the normal activity of neurotransmitters, the brain's chemical messengers.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
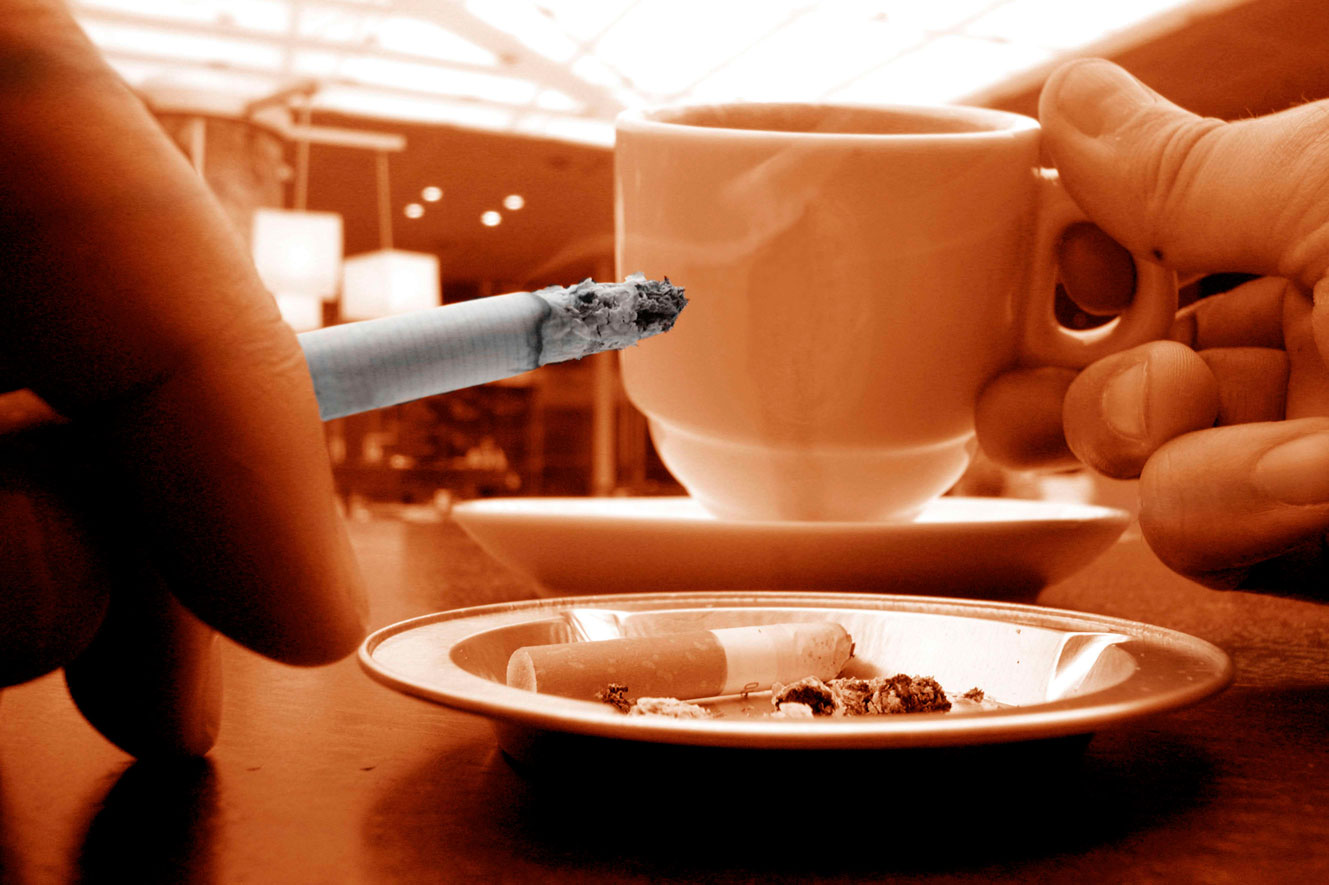

2. Stimulants (such as caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, and amphetamines) excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
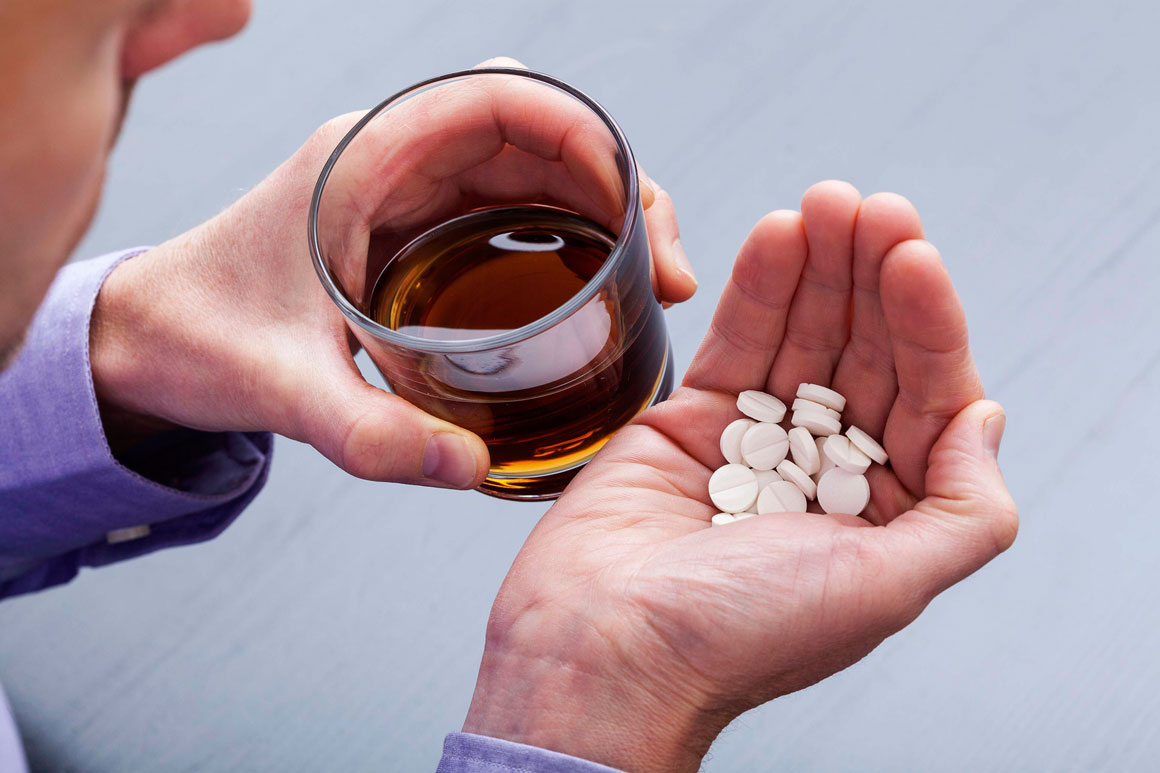

3. Depressants (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) reduce neural activity and slow body functions.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

4. Hallucinogens (such as LSD, PCP, and marijuana) distort perceptions and may produce hallucinations.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

5. In addition, other psychoactive drugs are used to treat specific psychological disorders. For example, antidepressant drugs boost a person's mood, usually by increasing the availability of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.

6. Antipsychotic drugs suppress some of the bizarre behaviors of schizophrenia, such as hearing imaginary voices. These drugs typically work by blocking the effects of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Review
Review
Select the NEXT button to continue with the Review.
7. Continued use of any psychoactive drug produces tolerance (requiring larger doses to produce the same effects), and may lead to dependence on the drug.
Practice : Types of Psychoactive Drugs
Practice: Types of Psychoactive Drugs
Roll over each term to view a brief definition of that type of drug.



depressants
stimulants
hallucinogens
Psychoactive drugs that slow down neural activity and body functions.
Examples: alcohol, barbiturates, opiates such as morphine, heroin, or oxycontin.
Psychoactive drugs that speed up neural activity and body functions.
Examples: caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines.
Psychoactive drugs that distort perception and may create hallucinations (false sensory experiences); also called psychedelic drugs.
Examples: LSD, marijuana (THC), mescaline.
Quiz 1
Quiz 1
Drag each drug type to the gray area in front of the appropriate description. When all the drug types have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.
Quiz 2
Quiz 2
Match the drug types to their scenarios by dragging each colored circle to the appropriate gray circle. When all the circles have been placed, select the CHECK ANSWER button.
Conclusion
