Chapter 7. Chapter 7: Population Ecology
What is carrying capacity...?

Guiding Question 7.4
What is carrying capacity, and why do some populations slowly approach it and then stabilize, whereas others overshoot it and then crash?
Why You Should Care
Carrying capacities are the theoretical maximum sustainable population sizes predicted by the amount of resources available. If you think back to past chapters, it should be easy to see why carrying capacities are important. Organizations like the United Nations are working hard to predict whether humans are overshooting their carrying capacity and how long it will take the global population to stabilize and to prepare for the possibility of a population crash. What does overshooting the carrying capacity look like for humans? There is a real possibility that we soon may not have enough water, farmland, or energy resources on a global scale for the human population. History tells us that, when resources are scarce on a local scale, large-scale social upheavals will ensue. Studying populations of other species will give us insight into our own.
Question Test Your Vocabulary
Fill in the blank with the correct term for each of the following definitions:
Fluctuations in population size that produce a very large population followed by a crash that lowers the size drastically, followed again by an increase to a large size and a subsequent crash, is known as a(n) 25gBex321fjyBfwKOFk3TARBmKil//X+.
The local extinction of a species is known as a(n) tlJnW7F+jbKfFiruCnCryg==.
Question 7.1
X5udeUNYwztOxb73lJqKyx3O6IDNdQQNqBwvKWkMCktdPs04MV9CQwZ0/SHpNC9MFGUmB5+WYyPNgv3j6pnsc5sSlzWlYv6vM22jdW1dNBlTf82L/vOlLf4bpL0BhGQPXSXkeAdhVmTw0O7MYfFDE8Z4lhQuLpOtxJL3meKUKek9cAIXaP6JzdVAFD3E5b5Vpu1ZEavjf09XFFyORldq3PzyUQZV+FIZjH7EOK9Q5NCrmNzDz8YHykO1y76i5P1x9Ab7zwpJSiysfR1VG8moRfVAnMkxcxbM421YCmjV3MQ96cKgExamine the idealized population growth curve below and answer the questions that follow:
Question 7.2
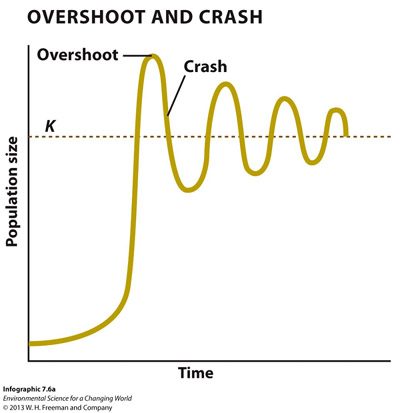
Are the factors that cause the crash after overshooting the carrying capacity more likely to be density independent or density dependent? E78g6WCDPKIoLqjH8p3ZqkcYsbqXcZEY1cYBDvedfr/D6dT1F2RyQS57ExA=
Question 7.3
Thought Questions: Explain two reasons that a crash could occur in a population of:
Bi/n3eBFqElzBC4o6UHWPPNkUYPQHUubN90GviFv7YpuDGJjMdrD7Jq3VQ8CXBXlCA98n2keRcvpa8+U 75sgukDevg57XZLxsQ3OfegkX1KDe5PKkTrA2ijSOHiPVl5kuvRAdkkFmSPXp/qC1ToLzg==B) Example of two plausible reasons: Predator populations will also suffer from having too much competition for food resources. They are also more susceptible to infectious disease.
Question 7.4
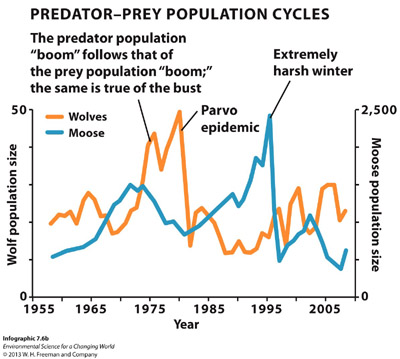
Examine the population data for wolves and moose on Isle Royale and answer the questions that follow: