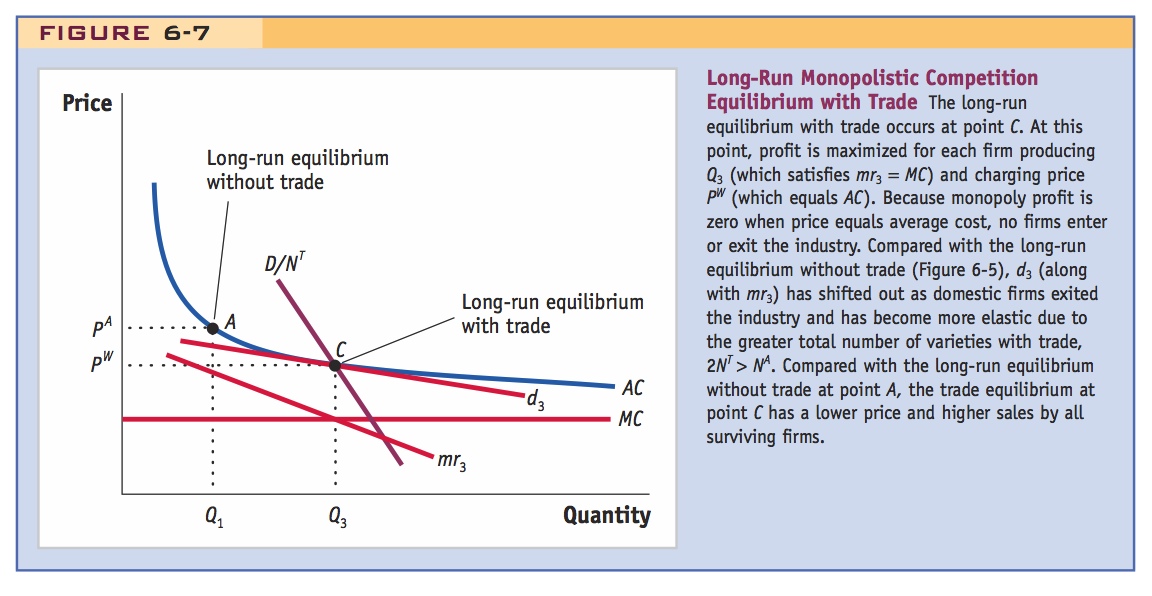
Long-Run Monopolistic Competition Equilibrium with Trade The long-run equilibrium with trade occurs at point C. At this point, profit is maximized for each firm producing Q3 (which satisfies mr3 = MC) and charging price PW (which equals AC). Because monopoly profit is zero when price equals average cost, no firms enter or exit the industry. Compared with the long-run equilibrium without trade (Figure 6-5), d3 (along with mr3) has shifted out as domestic firms exited the industry and has become more elastic due to the greater total number of varieties with trade, 2NT > NA. Compared with the long-run equilibrium without trade at point A, the trade equilibrium at point C has a lower price and higher sales by all surviving firms.