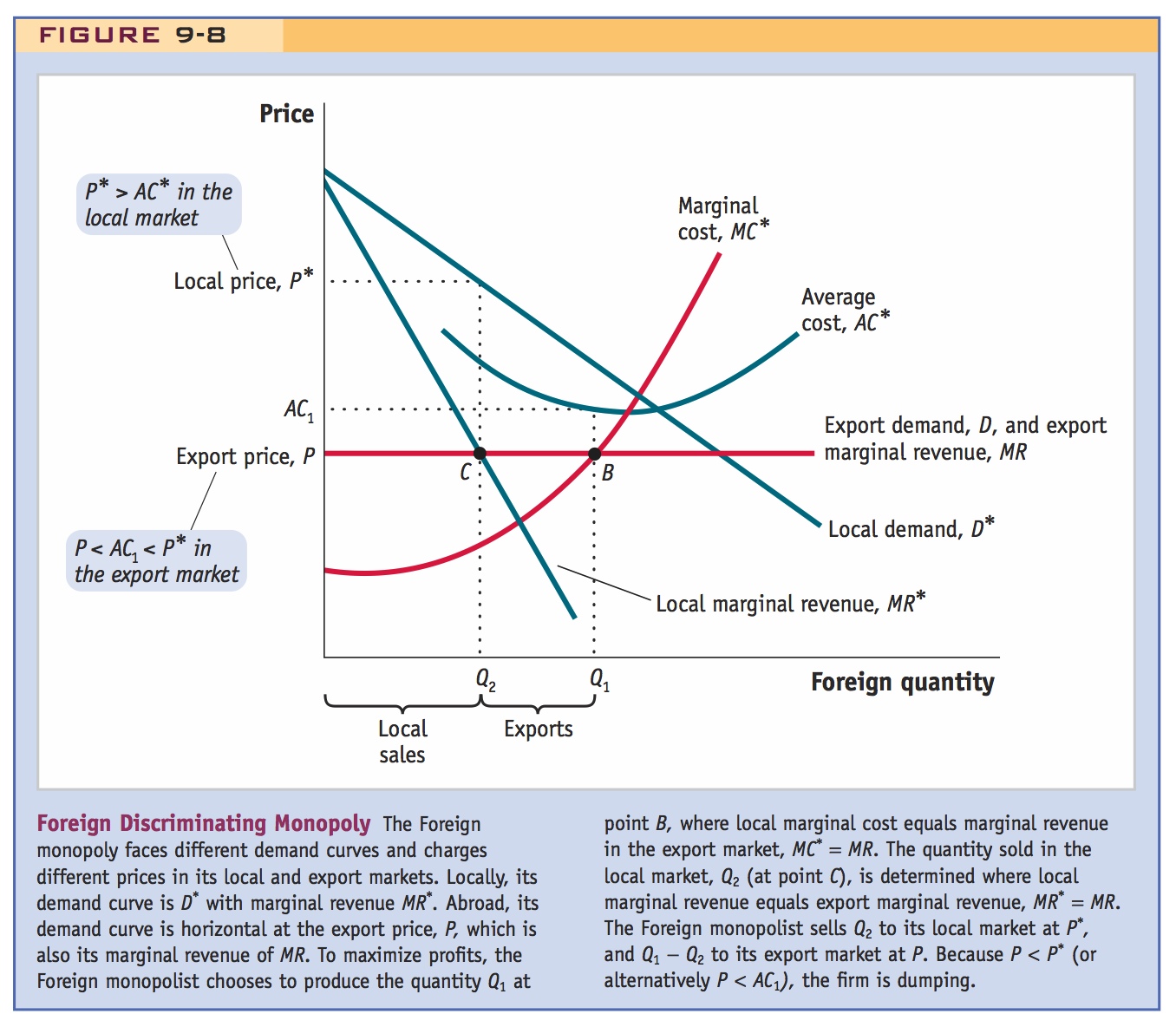
Foreign Discriminating Monopoly The Foreign monopoly faces different demand curves and charges different prices in its local and export markets. Locally, its demand curve is D* with marginal revenue MR*. Abroad, its demand curve is horizontal at the export price, P, which is also its marginal revenue of MR. To maximize profits, the Foreign monopolist chooses to produce the quantity Q1 at point B, where local marginal cost equals marginal revenue in the export market, MC* = MR. The quantity sold in the local market, Q2 (at point C), is determined where local marginal revenue equals export marginal revenue, MR* = MR. The Foreign monopolist sells Q2 to its local market at P*, and Q1 − Q2 to its export market at P. Because P < P* (or alternatively P < AC1), the firm is dumping.