Chapter 1. Absolute Threshold
1.1 Title slide

Absolute Threshold
Determine your absolute threshold for visual stimuli, using the method of constant stimuli and the staircase method.
CLICK ANYWHERE TO BEGIN
Photo: © M.Sobreira / Alamy
How Are Psychophysical Methods Used to Measure the Absolute Threshold?
In the method of adjustment, the stimulus is presented at an intensity well below or above the presumed threshold, and the participant adjusts the intensity until the stimulus is just detectable or just undetectable. The intensity at which each adjustment ends is taken as an estimate of the absolute threshold. The average of these estimates is taken as the final estimate of the absolute threshold. However, the method of adjustment is rarely used because the results tend to vary quite a bit.
The method of constant stimuli gives more consistent and reliable results. This method uses stimuli covering a range of intensity values likely to include the absolute threshold. The stimuli are presented in random order, and the participant indicates whether each stimulus was detected or not. The frequency with which each intensity was detected is plotted on a graph, and the resulting curve is used to estimate the absolute threshold (often defined as the intensity at which the participant detected the stimulus 50% of the time).
The staircase method is a more efficient version of the method of constant stimuli, also using stimuli covering a range of intensity values likely to include the absolute threshold. But in the staircase method, if a stimulus is detected, the intensity of the next stimulus is one step down; and if a stimulus isn't detected, the next stimulus is one step up. This means that, after the first few trials, the intensities of the presented stimuli tend to be near the absolute threshold. The mean of the intensities at which the participant's judgments "reverse" (i.e., change from detected to not detected or vice versa) is taken as an estimate of the absolute threshold.
1.2 Explain - custom
using two psychophysical methods: the method of constant stimuli and the staircase method.
1.3 Intro Experement 1
In this part of the demonstration, you'll use the method of constant stimuli to determine your
absolute threshold for detecting a spot of blue light against a black background.
1.4 Experement 1
In this part of the demonstration, you'll use the method of constant stimuli to determine your
absolute threshold for detecting a spot of blue light against a black background.
1.5 Experement 1 Result
Results
To see your results, go back and complete a new sequences of trials.
Estimated absolute threshold: n/a
Stimuli with relative intensities of 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 were presented 6 times each in random order. The plotted points show the percentage of 'Y' responses for each intensity. The curve is the psychometric function that best fits the plotted points. By definition, the estimated absolute threshold is the intensity at which you would be expected to detect the stimulus 50% of the time - that is, the intensity at which the
psychometric function is at 50%, as indicated by the green arrow.
Note: In laboratory experiments using the method of constant stimuli, participants' responses typically fit an S-shaped psychometric function like the one shown here. In this demonstration, done under much less controlled conditions, your responses are less likely to fit a smooth S-shaped curve.
1.6 Intro Experement 2
In this part of the demonstration, you'll use the staircase method to determine your
absolute threshold for detecting a spot of blue light against a black background.
1.7 Experement 2
In this part of the demonstration, you'll use the staircase method to determine your
absolute threshold for detecting a spot of blue light against a black background.
1.8 Experement 2 Result
Results
To see your results, go back and complete a new sequences of trials.
"N" response
Reversal
Estimated absolute threshold: n/a
Stimuli were presented at a range of intensities. Each time you responded Y the intensity was reduced, and each time you responded N the intensity was increased. After 30 trials or 8 Y/N reversals, the run of trials ended. The estimated absolute threshold is the average of the intensities at the n/a reversal points.
1.9 Explain
How Are Psychophysical Methods Used to Measure the Absolute Threshold?
The absolute threshold is the minimum intensity of a physical stimulus that can just be detected. Three methods used to measure absolute thresholds are the method of adjustment, the method of constant stimuli, and the staircase method. (The method of adjustment isn't covered in this demonstration.)
In the method of adjustment, the stimulus is presented at an intensity well below or above the presumed threshold, and the participant adjusts the intensity until the stimulus is just detectable or just undetectable. The intensity at which each adjustment ends is taken as an estimate of the absolute threshold. The average of these estimates is taken as the final estimate of the absolute threshold. However, the method of adjustment is rarely used because the results tend to vary quite a bit.
The method of constant stimuli gives more consistent and reliable results. This method uses stimuli covering a range of intensity values likely to include the absolute threshold. The stimuli are presented in random order, and the participant indicates whether each stimulus was detected or not. The frequency with which each intensity was detected is plotted on a graph, and the resulting curve is used to estimate the absolute threshold (often defined as the intensity at which the participant detected the stimulus 50% of the time).
The staircase method is a more efficient version of the method of constant stimuli, also using stimuli covering a range of intensity values likely to include the absolute threshold. But in the staircase method, if a stimulus is detected, the intensity of the next stimulus is one step down; and if a stimulus isn't detected, the next stimulus is one step up. This means that, after the first few trials, the intensities of the presented stimuli tend to be near the absolute threshold. The mean of the intensities at which the participant's judgments "reverse" (i.e., change from detected to not detected or vice versa) is taken as an estimate of the absolute threshold.
1.10 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
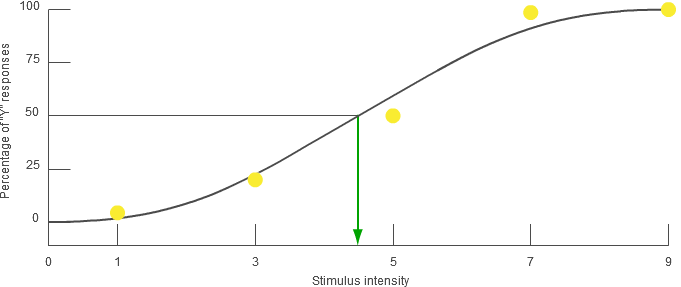
The graph above shows the results of using the method of constant stimuli to measure the absolute threshold. What is the approximate absolute threshold indicated by these results?
The correct answer is B.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
1.11 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
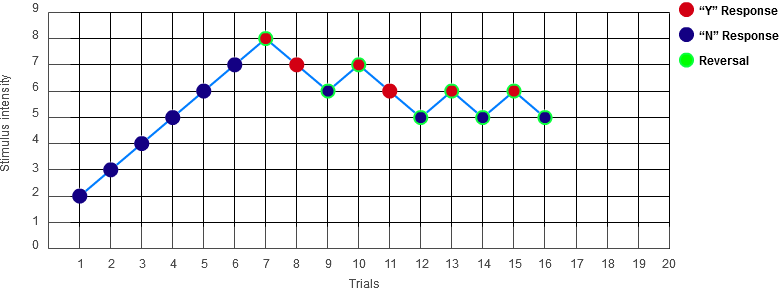
The graph above shows the results of using the staircase method to measure the absolute threshold. What is the approximate absolute threshold indicated by these results?
The correct answer is A.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
1.12 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
In which of the following psychophysical methods does the participant's response to a stimulus determine the relative intensity of the next stimulus?
The correct answer is B.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
1.13 Test - single choice
Select your answer to the question below. Then click SUBMIT.
Consider this statement: "After a few trials, the intensities of the presented stimuli tend to be close to the absolute threshold." This is true of which psychophysical method(s)?
The correct answer is C.
Click EXPLAIN if you want to review this topic.
1.14 Activity completed
Absolute Threshold.