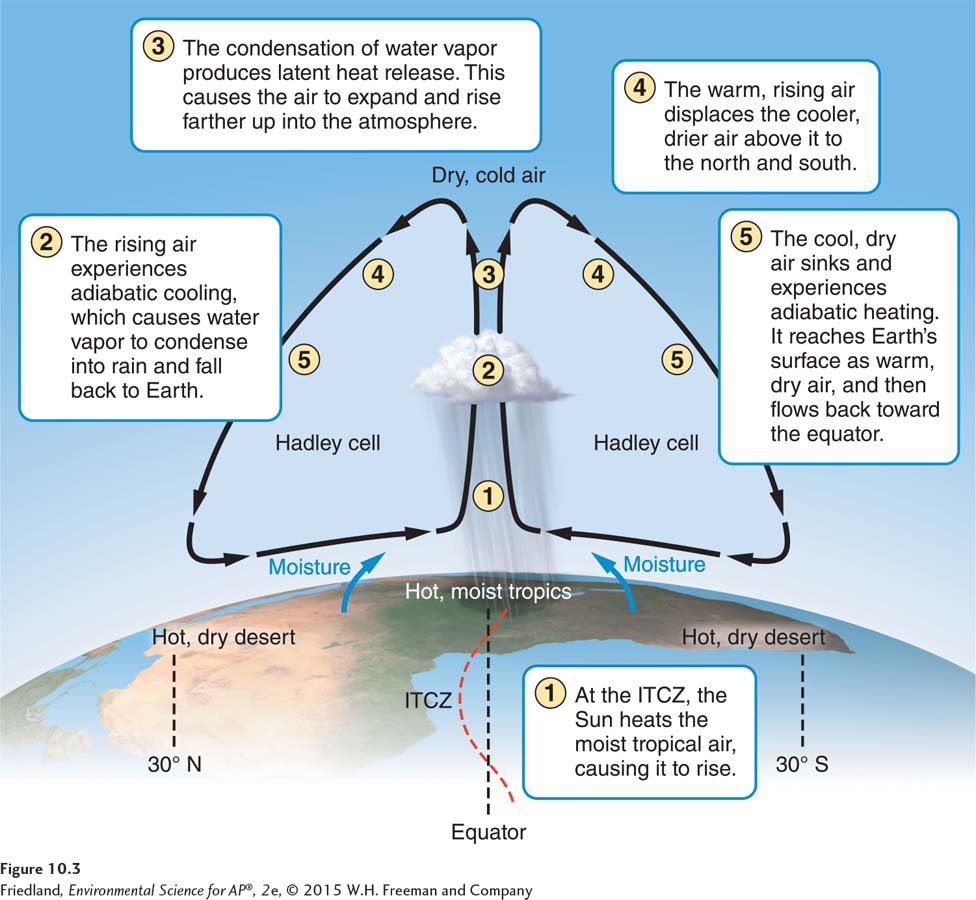
FIGURE 10.3 Hadley cells. Hadley cells are atmospheric convection currents that operate between the equator and 30° N and 30° S. Solar energy warms humid air in the tropics. The warm air rises and eventually cools below its saturation point. The water vapor it contains condenses into clouds and precipitation. The air, which now contains little moisture, sinks to Earth’s surface at approximately 30° N and 30° S. As the air descends, it is warmed by adiabatic heating. This descent of hot, dry air causes desert environments to develop at those latitudes.