Chapter 11 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 1
1. Which of the following does NOT explain the rise of the modern farming system?
The cost of labor varies from country to country.
Small farms are usually more profitable than large farms.
Irrigation contributes to greater crop yields.
Fertilizers improve crop yields and are easy to apply.
Mechanization facilitates monocropping and improves profits.
Question 2
2. Irrigation can result in which of the following environmental problems?
Reduction of evaporation rates
Accumulation of salts in soil
Waterlogging of soil and plant roots
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Question 3
3. The use of synthetic fertilizers increases crop yields, but also
destroys the nitrifying bacteria in the soil.
increases fish populations in nearby streams.
decreases phosphorus concentrations in the atmosphere.
increases nutrient runoff into bordering surface waters.
slows the release of organic nutrients from compost.
Question 4
4. Which of the following statements best describes the pesticide treadmill?
Broad-
spectrum pesticides degrade into selective pesticides, thereby killing a wide range of insect pests over a long period. Pesticides accumulate in the fatty tissues of consumers and increase in concentration as they move up the food chain.
Some pest populations evolve resistance to pesticides, which become less effective over time so that new pesticides must be developed.
Beneficial insects and natural predators are killed at a faster rate than the pest insects.
Testing of the toxicity of pesticides to humans cannot keep pace with the discovery and production of new pesticides.
Question 5
5. In which of the following ways did the Green Revolution increase food production?
The development of disease-
resistant and high- yielding crop plants Monocropping and the widespread use of machinery
The application of fertilizers and the use of irrigation techniques
I only
II only
III only
I and III
I, II, and III
Question 6
6. Which of the following is NOT a traditional farming technique that is used in sustainable agriculture?
Nomadic herding
Intercropping
Crop rotation
Agroforestry
Contour plowing
Question 7
7. Which of the following is an environmental advantage of no-
The use of herbicides improves the stability of the soil.
Migratory bird populations are reduced.
The undisturbed soil is less susceptible to erosion.
The crop residues reduce the soil profile.
The concentration of CO2 in the fields is increased.
Question 8
8. Which of the following practices is NOT a part of integrated pest management?
Crop rotation
Elimination of pesticides
Use of pest-
resistant crops Introduction of predators
Frequent inspection of crops
Question 9
9. Farmers who practice organic agriculture have less of an impact on the environment than farmers who practice industrial agriculture because they
use no-
till agriculture exclusively. import soil to maintain soil fertility.
maintain large farms with a single crop.
avoid pesticides and synthetic fertilizers.
have lower labor costs.
Question 10
10.Critics of using genetically modified organisms as food crops warn of which of the following dangers?
Introduction of new allergens into the food supply
Loss of genetic diversity in food crops
Decreases in food production worldwide
I only
II only
III only
I and II
I and III
Question 11
11.Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) can best be described as
facilities where a large number of animals are housed and fed in a confined space.
a method of producing more meat at a higher cost.
a means of producing great quantities of manure to fertilize fields organically.
an experimental plan to test the effectiveness of antibiotics.
the storing and compacting of grain for use as a nutrient supplement for cattle.
Question 12
12.Which of the following is NOT an environmental or health problem that has been associated with CAFOs?
The increase of antibiotic-
resistant bacteria potentially harmful to humans The overgrazing of large tracts of land
The runoff of animal wastes into natural waters
The production of huge quantities of manure, creating a waste disposal problem
The use of grain as feed, reducing the food supply available to humans
Use the following graphs to answer Question 13.
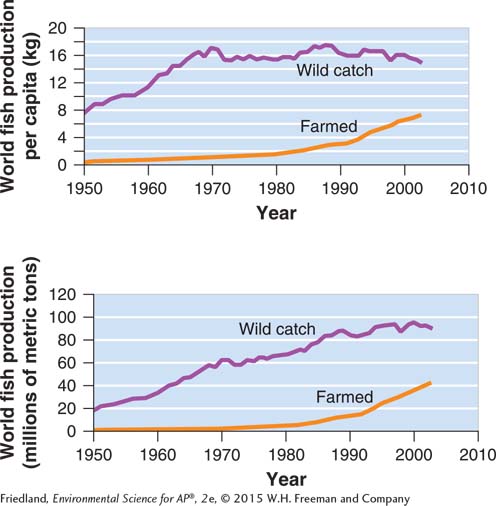
Question 13
13.The data presented in the graphs, compiled by the FAO, describe world fish production from 1950 to 2003. Based on these data, which of the following statements best describes the global trend in fish production?
The U.S. Sustainable Fisheries Act of 1996 has successfully banned the catch of threatened fish species.
The use of individual transferrable quotas (ITQs) has led to the overfishing of wild species.
Fish production through aquaculture exceeds fish production in the ocean.
As the human population continues to increase, the per capita wild catch also continues to increase.
As the human population continues to increase, per capita farmed fish production also continues to increase.
388
Question 14
14.Which of the following is an environmental effect of bycatch?
Juvenile fish are too small and slip through the nets, thereby ensuring the next generation of commercial fish.
Predators caught in the nets feed on the commercially important fish also caught, thereby reducing the total catch.
Nontarget fish populations have declined.
Cod populations have increased due to the removal of competitor species.
Endangered species, such as sea turtles, are being marketed through the ITQ system.
Question 15
15.It has been projected that aquaculture could supply about one-
concentrated waste from aquaculture facilities contaminates rivers and oceans.
raising fish in a protected environment could lead to a fish population overshoot.
the economies of developing countries would be negatively affected.
ocean fishing operations would go out of business.
the ITQ system would prohibit their expansion.
Question 16
16.What is the primary benefit of perennial plants?
Increased crop yields
Decreased pesticide use
Increased nitrogen fixing
Easy integration of crop rotation
Decreased erosion
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 1
1. Maintaining dairy cattle in a CAFO requires large quantities of water and produces vast quantities of wastewater and manure. The increasing number of CAFO dairies in eastern New Mexico and west Texas is contributing to significant groundwater contamination and the depletion of the Ogallala aquifer. Consider a CAFO with 1,000 dairy cows and answer the following questions.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the average dairy cow can consume up to 200 L of water daily. An additional 120 L per cow per day is required to wash the milking equipment and milking area. How many liters of water are required to operate this dairy daily? (2 points)
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the average dairy cow produces 55 kg of wet manure daily. How many metric tons would this dairy produce each day (1,000 kg = 1 metric ton)? (2 points)
Question 2
2. The table below shows the results of a survey of 113 people conducted in Trinidad, West Indies. It appeared in a 2006 issue of the British Food Journal.
Considering the “very” and “somewhat” responses as one group and the “not too” and “not at all” responses as another group, what percentage of the survey respondents would probably purchase GM foods? What percentage would not? (1 point)
Referring to the second survey question, identify and explain two possible benefits of the inclusion of GM foods in the diet that might convince people to purchase these products. (4 points)
Referring to the third survey question, identify and explain two possible dangers of the use of GM foods that might convince people not to purchase these products. (4 points)
Identify one U.S. federal agency that is responsible for the regulation of GMOs. (1 point)
| Questions | Very likely (%) | Somewhat likely (%) | Not too likely (%) | Not at all likely (%) |
| Would you be willing to purchase these foods (corn oil, potatoes, tomatoes, rice) which are bought regularly if they were genetically modified? | 15.9 | 31.9 | 38.9 | 7.1 |
| Would you purchase GM foods if they were considered healthier than conventionally produced foods? | 30.1 | 34.5 | 25.6 | 9.7 |
| Would you be willing to purchase GM foods if they were safe? | 15.9 | 31.9 | 38.9 | 7.1 |