Chapter 20 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 1
1. Based on the supply and demand curve below, which of the following can be inferred?
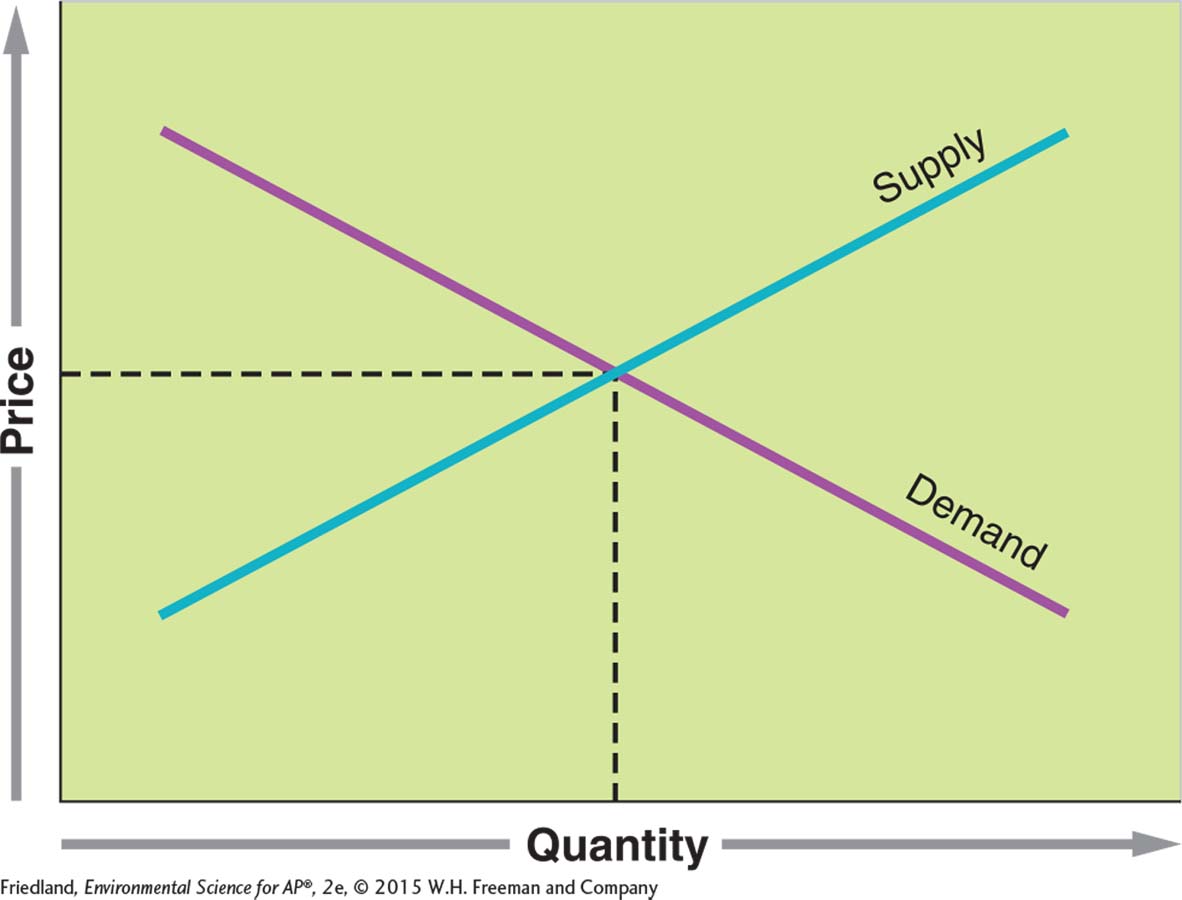
A lower price results in a greater demand.
A higher price results in a greater supply.
Price changes as supply and demand fluctuate.
I only
II only
III only
I and II
I, II, and III
Question 2
2. All of the following are examples of negative externalities except
global climate change as a result of greenhouse gas emissions from burning coal, oil, and gasoline.
increased pollination rates of crop plants as a result of local beekeeping.
a pulp mill that produces paper and pollutes the surrounding water and air.
runoff of pesticides and fertilizers from a farm into a nearby river.
acid deposition in the Adirondacks as a result of coal-
burning power plants in the Midwest.
Question 3
3. The genuine progress indicator (GPI) is more representative measure of the wealth and well-
measures productivity and consumption without taking externalities into account.
has risen in the United States while the GDP has remained fairly constant since 1970.
includes resource depletion, pollution, and health of the population in its calculation.
can be increased by higher health care costs and a greater incidence of illnesses.
does not reflect personal consumption, income distribution, or levels of higher education.
725
Question 4
4. Economic assets are the sum total of
Natural capital
Human capital
Manufactured capital
II only
III only
I and III
I, II, and III
Question 5
5. Valuation, according to environmental and ecological economics, would include all of the following except
the revenue generated from tourists visiting a national park.
the cost of wastewater treatment provided by a natural wetland.
the benefits derived from medicinal plants found in tropical rainforests.
the profits realized from hiring more employees to increase production.
the cost of converting animal wastes into reusable organic matter by detritivores.
Question 6
6. Full cost pricing by the internalization of externalities could result in which of the following?
Higher prices and a reduction in the consumption of items with high negative impacts
Lower prices and an increase in the consumption of items with high negative impacts
Greater consumer demand for products with high negative impacts
Lower production costs due to diminishing natural resources
Reduced production of environmentally friendly goods and services
Question 7
7. Cradle–
changes in the use of a product from one generation to the next.
life cycle of a product from its production to use to ultimate disposal.
use of resource extraction over the use of ecosystem services.
options for the disposal of solid waste generated by the product.
natural and human resources required for production.
Question 8
8. Recently the Los Angeles Unified School District adopted a new policy on the use of pesticides in schools. This policy assumes that the use of pesticides constitutes a risk to the health of children and the environment. Pesticides will be employed only after nonchemical methods have been explored. The pest control measure that is the least harmful will be implemented. This is an example of
the precautionary principle.
ecosystem services.
a market-
driven approach. sustainable use.
full cost pricing.
Question 9
9. Which is a United Nations organization concerned with the environment?
World Resources Institute (WRI)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Department of Energy (DOE)
World Health Organization (WHO)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Question 10
10.Which U.S. law contributes to sustainability by governing the tracking and disposal of solid and hazardous waste?
National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA)
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
Clean Water Act (CWA)
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)
Question 11
11.Strategies to implement environmental laws and regulations include all of the following except
standards for emission levels with fines when these levels are exceeded.
green taxes on environmentally harmful activities or emissions.
buying and selling of pollution permits.
an incentive-
based approach based on profits. banning the cap-
and- trade practice.
Question 12
12.Which is a harmful effect of poverty?
Decrease in unsanitary conditions
Greater access to clean drinking water
Increased overuse of the land
Decreased malnutrition
Lower infant mortality rates
Question 13
13.The United Nations Millennium Declaration proposes to meet which of the following goals?
Reduce environmental sustainability through economic development
Eliminate extreme poverty and hunger and reduce child mortality
Empower women and improve maternal health
I only
II only
IIII only
I and III
II and III
726
Question 14
14.The following is a summary report for the Distribution of Environmental Burdens for Allegheny County in Pennsylvania.
| Population categories | Number of facilities emitting criteria air pollutants per square mile |
| Minorities | 11 |
| Whites | 4.5 |
| Low- |
8 |
| High- |
3.9 |
| Families below poverty threshold | 8.9 |
| Families above poverty threshold | 4.1 |
| Non- |
6.9 |
| High school graduates | 4.7 |
The information in this table reflects
an environmental equity issue.
an anthropocentric worldview.
a biocentric worldview.
an ecocentric worldview.
a stewardship school issue.
Question 15
15.The idea that all people regardless of ethnic or socioeconomic status deserve equal environmental conditions is a central principle of
the triple bottom line.
the National Environmental Policy Act.
the United Nations Environment Programme.
environmental justice.
the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 1
1. Use the following information about gasoline consumption in the United States to answer the questions below.
In 2008 the United States consumed approximately 138 billion gallons of gasoline.
The current federal tax on gasoline is 18.4 cents per gallon.
The national average cost of a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline in June 2008 was $4.00 per gallon.
80 percent of the federal gasoline tax is used to subsidize road construction.
Calculate the total amount of money spent in the United States on the purchase of gasoline in 2008 (when gasoline cost $4.00 per gallon). (2 points)
What percent of the cost per gallon is the gasoline tax?
How much revenue was generated by the gasoline tax in 2008?
How much was used in 2008 to subsidize road construction? (3 points)
Does the federal tax on gasoline qualify as a green tax? Explain your answer. (1 point)
Advocates of raising the gasoline tax suggest that the tax be increased to 80 cents per gallon. Identify two economic effects and two environmental effects of raising this tax. (4 points)
Question 2
2. In 1997, the ecological economist Robert Costanza and his associates published a report titled The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. They estimated that if all the ecosystem services provided worldwide had to be paid for, the cost would average $33 trillion per year with a range from $16 trillion to $54 trillion. In that same year the global gross national product (GNP) was $18 trillion.
What is meant by ecosystem or ecological services? Give three specific examples and identify which United Nations organization might oversee these services. (4 points)
Define the term valuation. What would the worldwide consequences be if the world actually had to pay for ecosystem services and natural capital? (2 points)
Explain how this report could be used to develop a sustainable economic system. (2 points)
Which environmental worldview is most consistent with the concerns of environmental economics? Explain. (2 points)