101.1 Unit 2 AP® Environmental Science Practice Exam
180
Section 1: Multiple-
Choose the best answer for questions 1–
Question 101.1
1. Ecosystem boundaries are best defined as
borders that prevent migration or dispersal.
spatial divisions in abiotic and biotic conditions.
vague areas that often lack characteristic attributes.
the border of a lake or stream.
borders encompassing large areas of land or water.
Question 2 refers to the following diagram:
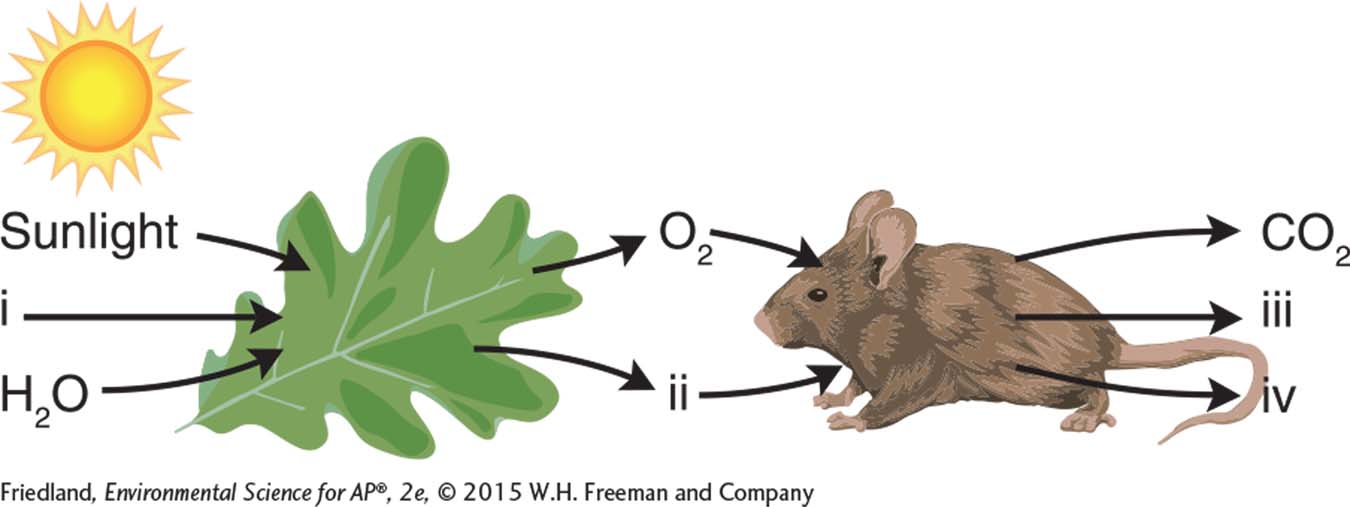
Question 101.2
2. By ingesting leaf tissue, herbivores utilize the products of photosynthesis for cellular respiration. The diagram above shows the flow of inputs and outputs for these two processes. Labels i, ii, iii, and iv refer to
CO2, C6H12O6, energy, and water.
CO2, CO2, energy, and excreted waste.
nutrients, C6H12O6, O2, and water.
CO2, C6H6O6, energy, and O2.
heat, organic tissue, energy, and O2.
Question 101.3
3. To estimate gross primary production, researchers can use all of the following variable combinations EXCEPT
net primary production and plant respiration.
standing crop, plant respiration, consumer biomass, and mass of consumer waste.
CO2 taken up by plant in sunlight and CO2 produced by plants in the dark.
CO2 released by plants in sunlight and CO2 produced by plants in the dark.
the amount of photosynthesis occurring over time.
Question 101.4
4. Which explains why the distribution of biomass in ecosystems is often structured like a pyramid?
The second law of thermodynamics
Low ecological efficiency in natural ecosystems
Photosynthesis is more efficient than cellular respiration
I only
II only
I and II
I and III
I, II, and III
Question 101.5
5. Which process is NOT part of the carbon cycle?
Growth of algae in the open ocean
Combustion of fossil fuels
Weathering of mineral rock
Decomposition of organic material
Cellular respiration
Question 101.6
6. Production of synthetic fertilizers is an example of ______ and one process that enables plants to use fertilizer is ________.
nitrogen fixation/nitrification
nitrification/nitrogen fixation
nitrification/assimilation
denitrification/nitrification
mineralization/leaching
Question 101.7
7. Phosphorus is often limiting in aquatic environments because
phosphorus is in higher demand by aquatic organisms relative to all other minerals.
phosphorus is not easily leached from soils and rapidly precipitates in water.
weathering of rock is an extremely slow process.
human activity regularly absorbs phosphorus from aquatic environments.
phosphorus rarely changes form as it is cycled from land to water.
Question 101.8
8. Intertidal communities are frequently disturbed by storms that generate large waves. Following a period of intermediate wave disturbance, a group of researchers examined the species richness of north and south Pacific intertidal communities. Four days after the disturbance, they found that northern communities had returned to their original state whereas southern communities were still recovering. This result suggests that northern intertidal communities
have greater resilience.
have greater resistance.
follow predictions of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis.
have greater species richness.
experience more frequent disturbance.
Question 101.9
9. Which statement does NOT describe a function of ozone gas on Earth?
Ozone absorbs ultraviolet-
B radiation from the Sun. Ozone absorbs ultraviolet-
C radiation from the Sun. Ozone absorbs X-
ray radiation from the Sun. Ozone causes the upper stratosphere to become warmer than the lower stratosphere.
Ozone prevents DNA damage.
181
Question 101.10
10.If Earth’s axis of rotation were tilted at 45 degrees instead of 23.5 degrees, how many hours of daylight would the Northern Hemisphere receive during the March and September equinoxes?
0 hours
6 hours
12 hours
18 hours
24 hours
Question 101.11
11.Which order of processes results in the occurrence of hot and dry deserts at 30°S and 30°N latitudes?
Adiabatic cooling, condensation, latent heat release, adiabatic heating
Adiabatic heating, condensation, latent heat release, adiabatic cooling
Latent heat release, adiabatic cooling, air displacement, condensation
Condensation, adiabatic heating, adiabatic cooling, latent heat release
Air displacement, condensation, adiabatic heating, adiabatic cooling
Question 101.12
12.Lush vegetation on the western slopes of the Colorado Rockies may be attributed to
trade winds generated by the Coriolis effect.
a rain shadow.
adiabatic cooling.
I only
III only
I and II
I and III
I, II, and III
Question 101.13
13.The mixing of surface water and deep water in the oceans that occurs because of differences in salinity is known as
upwelling.
a gyre.
the El Niño–
Southern Oscillation. an isocline.
thermohaline circulation.
Question 101.14
14.Which of the following is NOT a cause of the El Niño–
The position of Australia with respect to South America
A reversal of trade wind direction
Movement of warm surface water from east to west
A buildup of warm water along the coast of South America
Upwelling of water along the coast of South America
Questions 15 and 16 refer to the following graph:
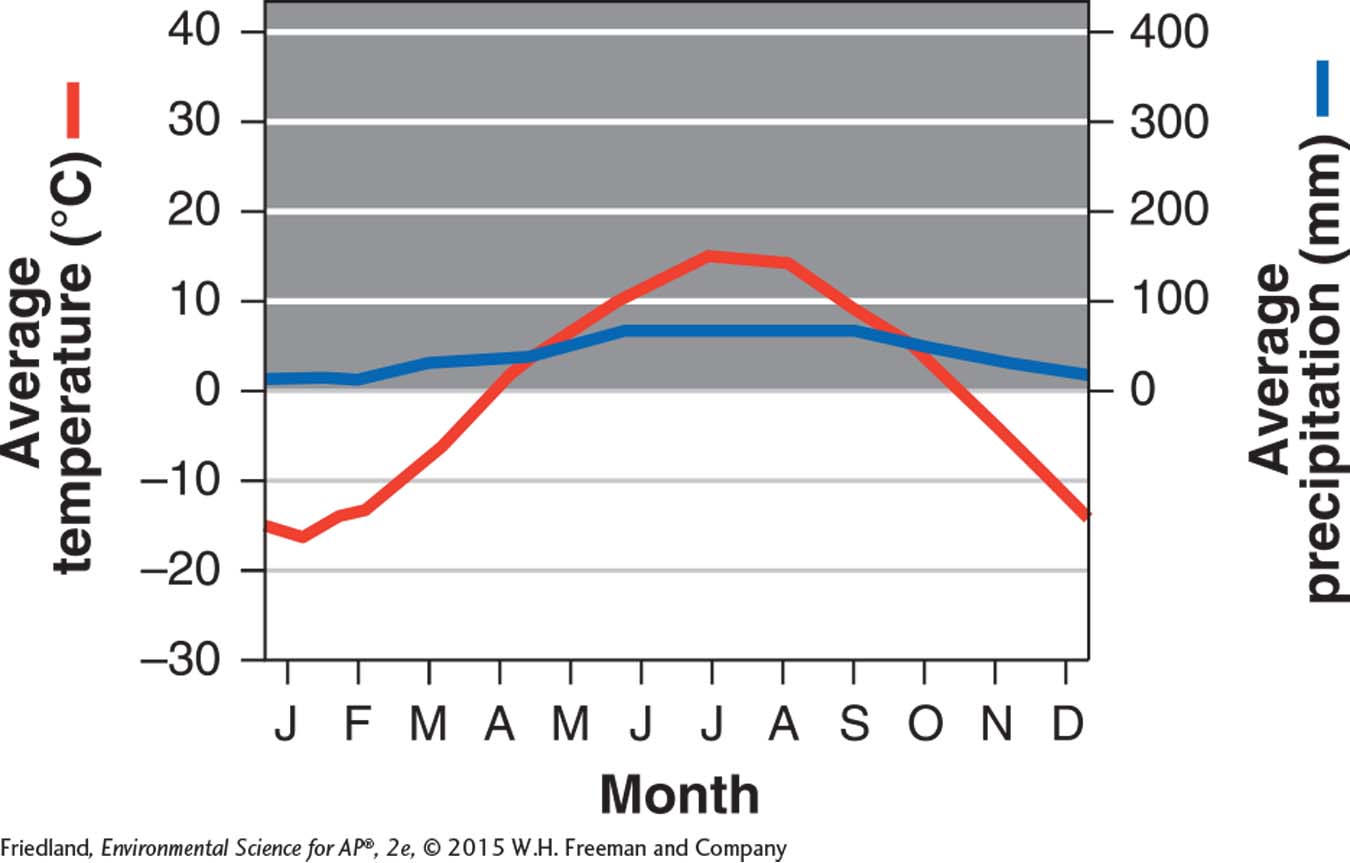
Question 101.15
15.For the region represented by the graph, when is the growing season?
January to December
January to July
April to October
November to March
July to December
Question 101.16
16.What biome is this graph most likely to represent?
Temperate rainforest
Boreal forest
Temperate seasonal forest
Tropical seasonal forest
Cold desert
Question 101.17
17.Which list contains terms for lake classification, from systems with the lowest primary productivity to systems with the highest primary productivity?
Eutrophic, mesotrophic, oligotrophic
Oligotrophic, eutrophic, mesotrophic
Mesotrophic, eutrophic, oligotrophic
Mesotrophic, oligotrophic, eutrophic
Oligotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic
Question 101.18
18.Iron is a limiting nutrient for algae in the open ocean. After researchers released 5,000 kg of iron into the ocean, they notice an algal bloom in the _______ zone.
photic
profundal
aphotic
intertidal
benthic
182
Question 19 refers to the following table comparing forest communities in different regions of North America.
Total percent statewide cover
| Species | Connecticut (CT) | Pennsylvania (PA) | Georgia (GA) |
| Red maple | 25 | 40 | 20 |
| Black oak | 30 | 20 | 50 |
| White pine | 15 | 10 | 10 |
| Eastern hemlock | 20 | 10 | 0 |
| Black cherry | 20 | 20 | 30 |
Question 101.19
19.Researchers collected data on tree abundance for a group of forest communities in the three states shown in the table above. Which statement best describes the forest communities within each state?
CT has the highest species richness; PA has the highest species evenness.
PA has the highest species richness; CT has the highest species evenness.
CT and PA have equal species richness; GA has the highest species evenness.
GA and PA have equal species richness; GA has the highest species evenness.
CT and PA have equal species richness; CT has the highest species evenness.
Question 101.20
20.Humans have developed varieties of grape vines that produce grapes that make fine wines if grown under particular environmental conditions. Therefore, the flavor of grapes on a given vine depends on
genes.
environments.
artificial selection.
I only
II only
III only
I and II
I, II, and III
Question 101.21
21.Which could cause a dramatic decline in genetic diversity?
Mutation
A bottleneck effect
A founder effect
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Question 101.22
22.Which is an example of sympatric speciation?
A stream diversion divides a single turtle population into two isolated populations that evolve into two species.
Forest fragmentation isolates two species of mice.
Two bird species from separate forests evolve reproductive isolation.
Two fish species in a single lake evolve from a single ancestor that once lived in the lake.
Artificial selection by humans for certain breeds of dog.
Question 101.23
23.Which of the following is the best definition of a realized niche?
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species can live
The total amount of area in which a species can live
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions under which a species actually lives
The total amount of area in which a species actually lives
The range of abiotic and biotic conditions in which a species can live but its predators cannot live
183
Section 2: Free-
Write your answer to each part clearly. Support your answers with relevant information and examples. Where calculations are required, show your work.
Question 101.24
1. In temperate forests, average daily temperatures during winter often drop to 0° C or lower. During this time, many organisms burrow into the soil and remain in a dormant stage until the spring thaw. Although these organisms are able to withstand very cold temperatures, they also rely on the insulating capacity of snow, which prevents soil from experiencing temperature extremes. However, during winters when snowfall is less abundant, soil is exposed to freezing temperatures that kill many of the bacteria and fungi residing in the very top layers of soil. When bacteria and fungi die, nutrients and other organic material are easily leached out of cell membranes and these materials enter the soil.
What are two consequences of reduced winter snowfall on the nitrogen cycle in temperate forests? (4 points)
What is one consequence of reduced winter snowfall on the carbon cycle in temperate forests? (2 points)
Describe two ways in which stream and pond food webs might be affected by reduced snowfall during the winter. (2 points)
Exposure of the soil to extreme temperatures can also kill larger organisms, such as frogs and burrowing insects. For example, wood frogs (Lithobates sylvaticus) that burrow too close to the soil surface are likely to die whereas frogs that burrow deeper in the soil are likely to survive. Describe one way in which reduced winter snowfall could alter the local population genetics of wood frogs. (2 points)
Question 101.25
2. During El Niño–
Draw a diagram that shows both Hadley and Ferrell cells, noting latitudinal locations, air direction and areas of condensation, adiabatic heating, and adiabatic cooling. (4 points)
Why would the western slopes of the southern Colorado Rockies experience greater precipitation than the eastern slopes? (2 points)
A researcher wants to test the hypothesis that gross primary productivity (GPP) on the western slopes of the Rockies is greater during ENSO years.
Write an equation that defines gross primary productivity. (1 point)
What characteristics of local plants should the researcher measure to test the hypothesis? Provide justification for your responses. (2 points)
Provide a null hypothesis for this study. (1 point)