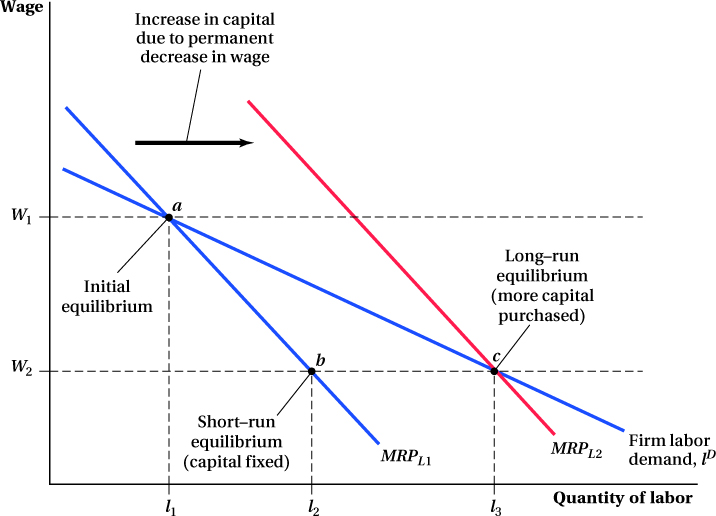
FIGURE 13.8 Short-Run and Long-Run Labor Demand
A firm facing a market wage W1 and having a short-run demand for labor given by MRPL1 initially hires labor quantity l1 (point a). The short-run effect of a permanent drop in the market equilibrium wage from W1 to W2 will cause the firm to hire more labor until MRPL1 equals W2. This is labor quantity l2 (point b). In the long run, the increase in labor hired to l2 raises the firm’s marginal product of capital, which leads the firm to purchase more capital and, in turn, raises the firm’s marginal revenue product of labor. This shifts out the firm’s short-run labor demand curve to MRPL2, and the firm hires additional labor until W2 = MRPL2. This is labor quantity l3 (point c). The long-run labor demand curve, ID, runs through points a and c.

