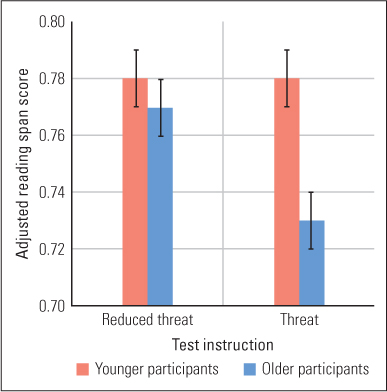
Figure 14.2: Stereotype threat in a working memory task Older (average age = 69) and younger (average age = 21) adults were given working-memory tests and told that these tests were “fully validated and diagnostic of memory capacity.” In the Threat condition, subjects were told that both younger and older adults would be performing these tasks, which is usually enough to remind older adults that memory is typically worse in older than younger adults. In the Reduced Threat condition, subjects were also told that these were “age-fair” tests in which performance does not vary with age. As you can see, the younger and older adults varied minimally in the Reduced Threat condition. In contrast, the older adults performed significantly worse in the Threat condition.
(Based on data from Mazerolle et al., 2012.)