FIGURE 6.2
Brehm’s Free Choice Paradigm
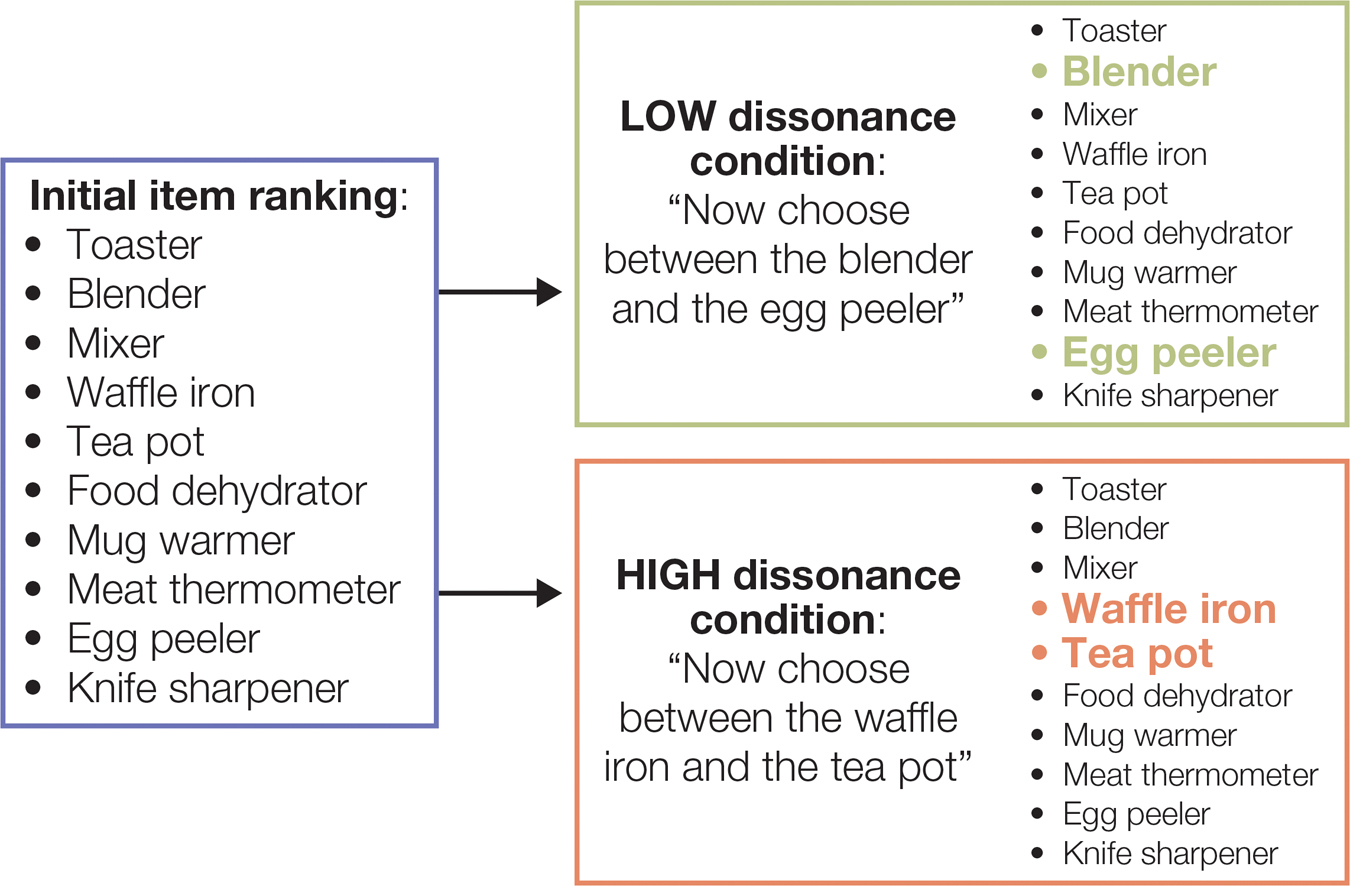
In the free choice paradigm (Brehm, 1956), participants in the high dissonance condition are asked to make a difficult choice between two similarly attractive options. Participants in the low dissonance condition make an easy choice between one attractive and one unattractive option. After making their choices, participants in the high dissonance condition increase their liking for what they chose and decrease their liking for what they didn’t choose, a spreading of alternatives.
Brehm’s Free Choice Paradigm
In the free choice paradigm (Brehm, 1956), participants in the high dissonance condition are asked to make a difficult choice between two similarly attractive options. Participants in the low dissonance condition make an easy choice between one attractive and one unattractive option. After making their choices, participants in the high dissonance condition increase their liking for what they chose and decrease their liking for what they didn’t choose, a spreading of alternatives.
[Research from Brehm (1956)]