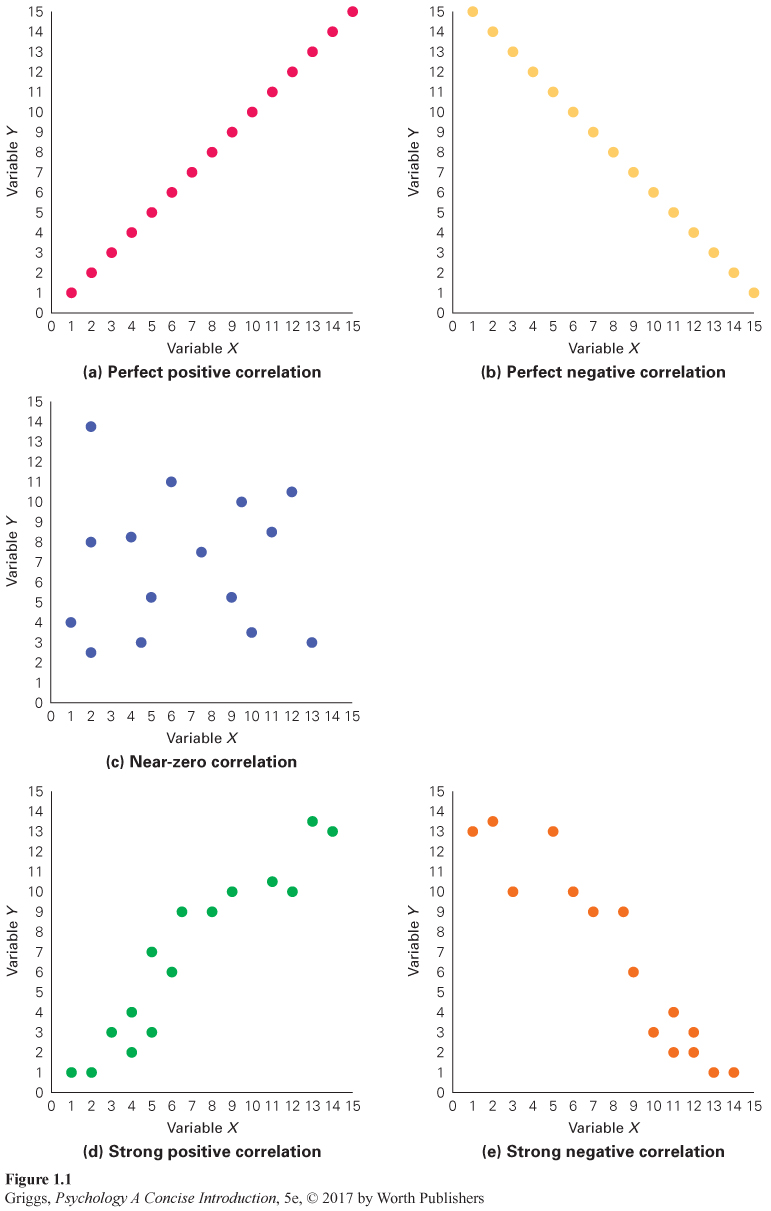
Figure 1.1 | Some Sample Scatterplots | (a) and (b) are examples of perfect correlations because there is no scatter— r-