CHAPTER SUMMARY
18.1 COMPLEX TRAITS ARE THOSE INFLUENCED BOTH BY THE ACTION OF MANY GENES AND BY ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS.
- Complex traits that are measured on a continuous scale, like human height, are called quantitative traits.
- It is usually difficult to assess the relative roles of genes and the environment (“nature” vs. “nurture”) in the production of a given trait in an individual, but it is reasonable to consider the relative roles of genetic and environmental variation in accounting for differences among individuals for a given trait.
- The relative importance of genes and environment in causing differences in phenotype among individuals differs among traits. For some traits (like height), genetic differences are the more important source of variation, whereas for others (such as cancer), environmental differences can be the more important.
- Genetic and environmental factors can interact in unpredictable ways, resulting in genotype-by-environment interactions.
18.2 GENETIC EFFECTS ON COMPLEX TRAITS ARE REFLECTED IN RESEMBLANCE BETWEEN RELATIVES.
- In an analysis of heights of parents and offspring, Galton observed regression toward the mean, in which the offspring exhibit an average phenotype that is less different from the population mean than that of the parents.
- “Heritability” refers to the proportion of the total variation in a trait that can be attributed to genetic differences among individuals.
- The heritability of the same trait can differ among populations because of differences in genotype or environment.
18.3 TWIN STUDIES HELP SEPARATE THE EFFECTS OF GENOTYPE AND ENVIRONMENT ON VARIATION IN A TRAIT.
- Monozygotic, or identical, twins result from the fertilization of a single egg and are genetically identical.
- Dizygotic, or fraternal, twins result from the fertilization of two eggs and are genetically related to each other in the same way that other siblings are related to each other.
- Concordance is the percentage of cases in which both members of a pair of twins show the trait when it is known that at least one member shows it.
- Comparisons of concordance rates of identical twins and concordance rates of fraternal twins can help to determine to what extent variation in a particular trait has a genetic component.
18.4 MANY COMMON DISEASES AND BIRTH DEFECTS ARE AFFECTED BY MULTIPLE GENETIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL RISK FACTORS.
- Complex traits are often influenced by many genes with multiple, interacting, and unequal effects.
- Hundreds of genes affect human height.
- Personalized medicine tailors treatment to an individual’s genetic makeup.
Self-Assessment Question 1
Give three examples of a complex trait.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Examples of a complex traits are height, weight, hair color, skin color, heart disease, diabetes, cancer, depression, high blood pressure, number of eggs laid by hens, milk production in dairy cows, and yield per acre of grain.
Self-Assessment Question 2
Explain why complex traits are often called quantitative traits.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Complex traits are often called quantitative traits because phenotype is measured along a continuum with only small intervals between similar individuals. In many complex traits the phenotype is determined by measurement.
Self-Assessment Question 3
Name several factors that influence variation in complex traits.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Several factors that can influence variation in complex traits are environmental factors like sunlight, moisture or nutrition, and genetic factors such as multiple genes affecting a single trait.
Self-Assessment Question 4
Explain why it does not make sense to try to separate the effects of genes (“nature”) and the environment (“nurture”) in a single individual.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
It does not make sense to try and separate the effects of genes and the environment in a single individual because they are so intimately related that it would be nearly impossible, and mostly meaningless, to split them apart.
Self-Assessment Question 5
Explain how you would go about determining the relative importance of genes and the environment for a particular trait.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Let’s say you wanted to test the effects of diet on diabetes development in two sets of mice with different genotypes. Fed a normal diet, the two mice strains have normal levels of blood glucose, but when fed a high-fat and sugar diet, one mouse genotype displays diabetic symptoms while the other does not. This experiment separates the environmental influence of diet on a particular complex trait, diabetes, and shows that both the environment and genotype are important for the development of disease.
Self-Assessment Question 6
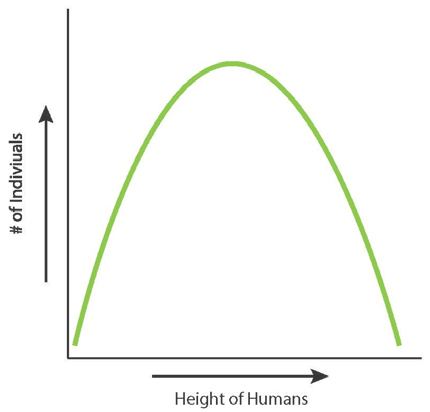
Graph a trait, like human height, with height on the x-axis and number of individuals on the y-axis, and describe the shape of the resulting graph.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
See attached graph. The resulting shape of the graph is called a bell-shaped curve or normal distribution.
Self-Assessment Question 7
Explain why the effect of a genotype on a phenotype cannot always be determined without knowing what the environment is, and why the effect of a particular environment on a phenotype cannot always be determined without knowing the underlying genotype.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
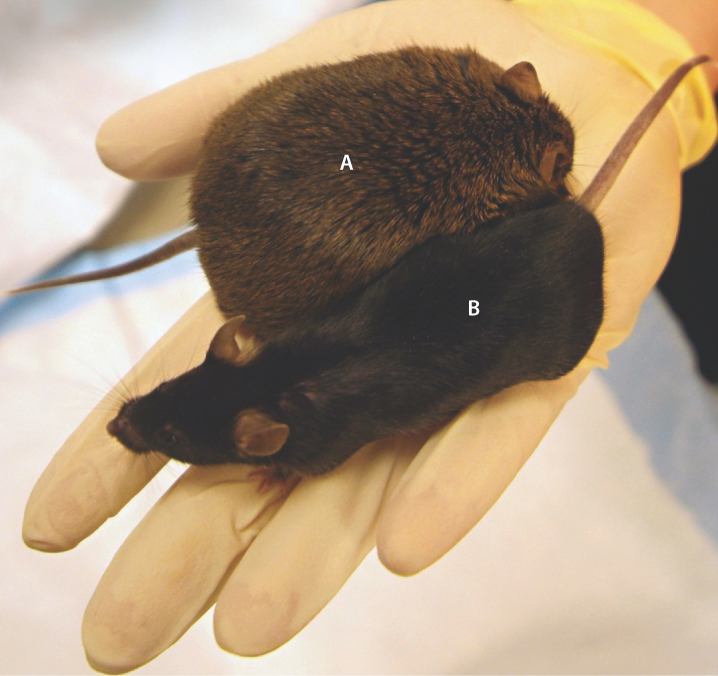
The effect of genotype on a phenotype cannot always be determined without knowing what the environment is and vice versa because in many cases you will not see a phenotype if both conditions are not represented. In the example of the obese mouse phenotype in Figure 18.6, you only get obese mice when both the underlying genotype is present and the mice are fed a high-fat diet (environment).
Self-Assessment Question 8
Define what is meant by “regression toward the mean.”
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Regression toward the mean explains that offspring exhibit an average phenotype that is less different from the population mean than that of their parents. Or, in other words, children of short parents tend to be closer to the population mean height (i.e., taller than their parents).
Self-Assessment Question 9
Define the “heritability” of a trait and explain why it depends on the population being studied.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Heritability of a trait is the proportion of the total variation due to genetic differences among individuals. Heritability depends on the population being studied because the influence of the environment and the genotypes of the populations are going to be different for different populations or even the same population at different times. Thus, these factors change the relative heritability of that complex trait.
Self-Assessment Question 10
Define “concordance” and explain how twin studies can be used to investigate the importance of genetic and environmental factors in the expression of a trait.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Concordance is defined as the percentage of cases in which both members of a pair of twins show the trait when it is known that at least one member shows it. Identical twin studies can be used to investigate the importance of environment and genetic factors in the expression of a trait because both twins have the same genotypes. The variable in this situation is the environment; the researcher must be able to tease apart effects of genes and environment on a particular trait.
Self-Assessment Question 11
For a typical complex trait, describe the relationship between the number of genes affecting the trait and the magnitude of their effects on the trait.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
When few genes contribute to a trait, each one typically has a large effect. Conversely, when many genes contribute to a trait, each one typically has a small effect.
Self-Assessment Question 12
Explain what personalized medicine is and how it relates to complex traits such as human diseases.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Personalized medicine is when the patient’s genotype for a particular disease is known and a treatment is matched specifically to the genetic risk factors of that patient.