CHAPTER SUMMARY
23.1 A PHYLOGENETIC TREE IS A REASONED HYPOTHESIS OF THE EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS OF ORGANISMS.
- The nested pattern of similarities seen among organisms is a result of descent with modification and can be represented as a phylogenetic tree.
- The order of branches on a phylogenetic tree indicates the sequence of events in time.
- Sister groups are more closely related to one another than they are to any other group.
- A node is a branching point on a tree, and it can be rotated without changing evolutionary relationships.
- A monophyletic group includes all the descendants of a common ancestor, and it is considered a natural grouping of organisms based on shared ancestry.
- A paraphyletic group includes some, but not all, of the descendants of a common ancestor.
- A polyphyletic group includes organisms from distinct lineages based on shared characters, but it does not include a common ancestor.
- Organisms are classified into domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
23.2 A PHYLOGENETIC TREE IS BUILT ON THE BASIS OF SHARED DERIVED CHARACTERS.
- Characters, or traits, existing in different states are used to build phylogenetic trees.
- Homologies are similarities based on shared ancestry, while analogies are similarities based on independent adaptations.
- Homologies can be ancestral, unique to a particular group, or present in some, but not all, of the descendants of a common ancestor (shared derived characters).
- Only shared derived characters, or synapomorphies, are useful in constructing a phylogenetic tree.
- Molecular data provide a wealth of characters that complement other types of characters in building phylogenetic trees.
- Phylogenetic trees can be used to understand evolutionary relationships of organisms and solve practical problems, such as how viruses evolve over time.
23.3 THE FOSSIL RECORD PROVIDES A DIRECT GLIMPSE OF EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY.
- Fossils are the remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary rocks.
- The fossil record is imperfect because fossilization requires burial in sediment, sediments accumulate episodically and discontinuously, and fossils typically preserve only the hard parts of organisms.
- Radioactive decay provides a means of dating rocks.
- Archaeopteryx and Tiktaalik are two fossil organisms that document, respectively, the bird–dinosaur transition and the fish–tetrapod transition.
- The history of life is characterized by rare mass extinctions, including the extinction at the end of the Cretaceous Period 65 million years ago in which the dinosaurs (other than birds) became extinct, and the extinction at the end of the Permian Period 252 million years ago, the largest documented mass extinction in the history of Earth.
23.4 PHYLOGENY AND FOSSILS PROVIDE INDEPENDENT AND CORROBORATING EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION.
- Phylogeny makes use of living organisms, and the fossil record supplies a record of species that no longer exist, absolute dates, and environmental context.
- Data from phylogeny and fossils are often in agreement, providing strong evidence for evolution.
Self-Assessment Question 1
Give two examples of a nested pattern of similarity among organisms.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Two examples of a nested pattern of similarity among organisms are (1) a dog and a wolf are more similar to each other than either is to a cat, and (2) a dog, a wolf, and a cat are more similar to each other than they are to a turtle.
Self-Assessment Question 2
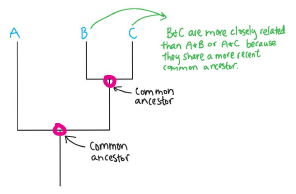
With reference to a phylogenetic tree, show how a nested pattern of similarity is the necessary result of evolution.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
See drawing.
Self-Assessment Question 3
Distinguish among monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups, and give an example of each.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Monophyletic groups are groups in which all members share a single common ancestor not shared with any other species or group of species, like amphibians. Paraphyletic groups include some, but not all, of the descendants of a common ancestor, like birds being excluded from the “reptile” group even though there is evidence that they share a common ancestor. A polyphyletic group does not include the last common ancestor of all members, like putting bats and birds in a single “flying vertebrates” group.
Self-Assessment Question 4
List the levels of classification, from the least inclusive (species) to the most inclusive (domain).
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
The levels of classification are as follows: species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain.
Self-Assessment Question 5
Describe two traits that are homologous and two that are analogous.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
A homologous trait is one that results from shared ancestry, such as an amniotic egg and lungs. An analogous trait is a similarity that results from convergent evolution, such as bird and bat wings or echolocation.
Self-Assessment Question 6
Name a type of homology that is useful in building phylogenetic trees and explain why this kind of homology, and not others, is useful.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Synapomorphies, or shared derived characters between some members of a group, are useful in building phylogenetic trees because the homologies are shared by some but not all of the members of the group. If an entire group shared the same homologous trait, we would not be able to construct a meaningful phylogenetic tree.
Self-Assessment Question 7
Name three types of fossil.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Three types of fossils are skeletal fossils, where the hard parts of the organism such as the skeleton are fossilized, trace fossils, where the tracks or trails of an animal are fossilized, and molecular fossils, where an organism's DNA or proteins are left.
Self-Assessment Question 8
Explain why there are gaps in the fossil record.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
For an organism to be fossilized it must be buried and have features that resist decay after death. Not all organisms meet these two criteria, so they do not become fossils and lead to gaps in the fossil record.
Self-Assessment Question 9
Explain how the fossil record can be used to determine both the relative and the absolute timescales of past events.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
The relative timescale of past events can be determined by the location of the fossil in the Earth’s surface since a fossil’s age is related to how deep into the Earth’s layers the fossil is found. The absolute timescale can be determined by measuring isotope decay, since unstable isotopes decay at a particular, known rate. Carbon, uranium, and lead are all used to date fossils.
Self-Assessment Question 10
Describe the significance of Archeopteryx and Tiktaalik.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Archeopteryx is a fossil organism that shows the transition from bird to dinosaur, and Tiktaalik is a fossil organism that shows the transition from fish to tetrapod in the fossil record. Transition fossils are significant because they give us evolutionary clues of morphological and physiological phylogenetic shifts through time.
Self-Assessment Question 11
Describe how mass extinctions have shaped the ecological landscape.
Show Model Answer
Model Answer:
Mass extinctions have shaped the ecological landscape by removing the dominant species in an ecosystem and thereby changing the competitive landscape of the remaining organisms. The survivors of this altered ecosystem live and reproduce, thus introducing new mutations into the population.