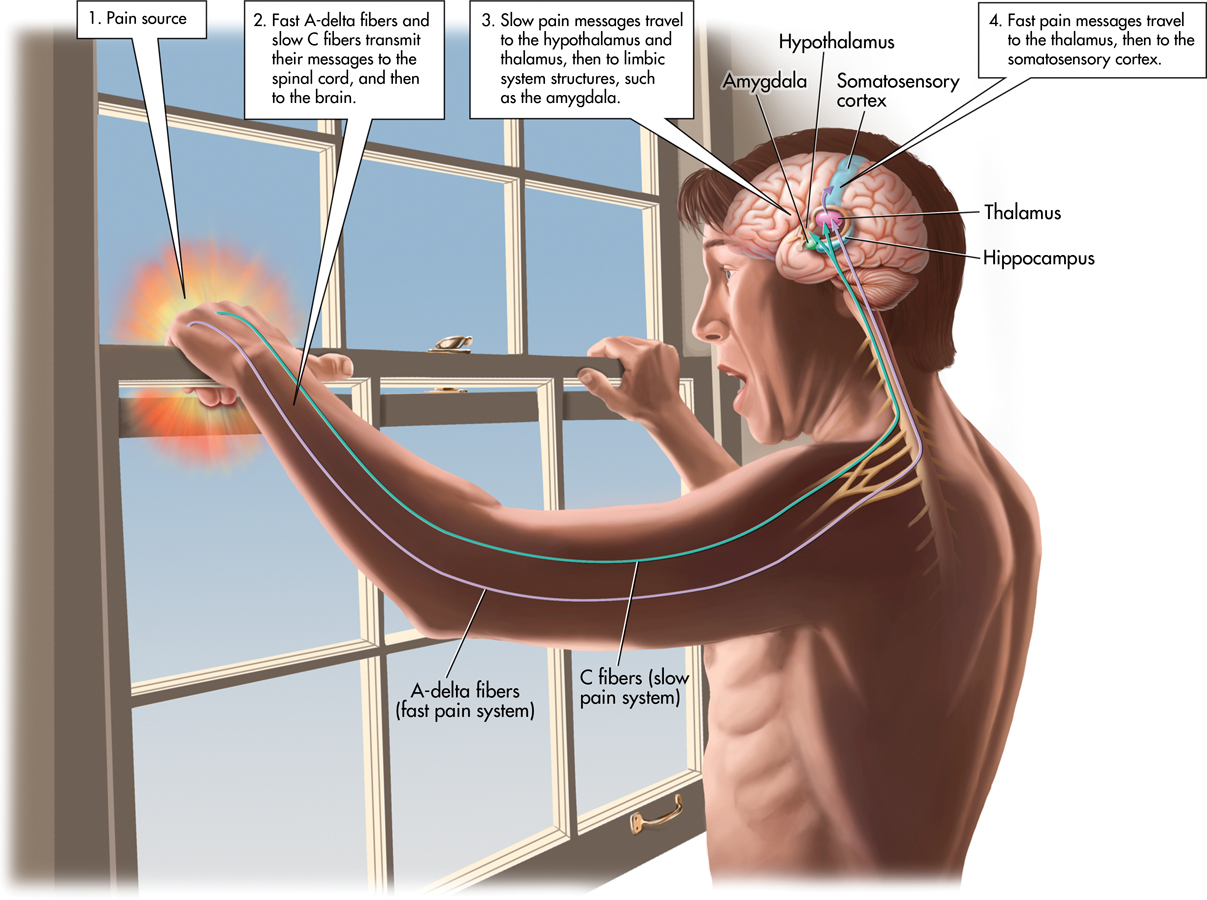
FIGURE 3.11 Fast and Slow Pain Pathways The fast pain pathway consists of myelinated A-delta fibers, shown in purple, which project first to the thalamus and then on to the somatosensory cortex. Signals carried along this pathway produce the sensory aspects of pain—the sharp but short-lived pain of an immediate injury. In contrast, the slow pain pathway consists of unmyelinated C fibers, shown in green. The slow pain pathway is much more involved with the emotional aspects of pain. The C fibers project to the thalamus and hypothalamus, then to limbic system structures, including the amygdala.