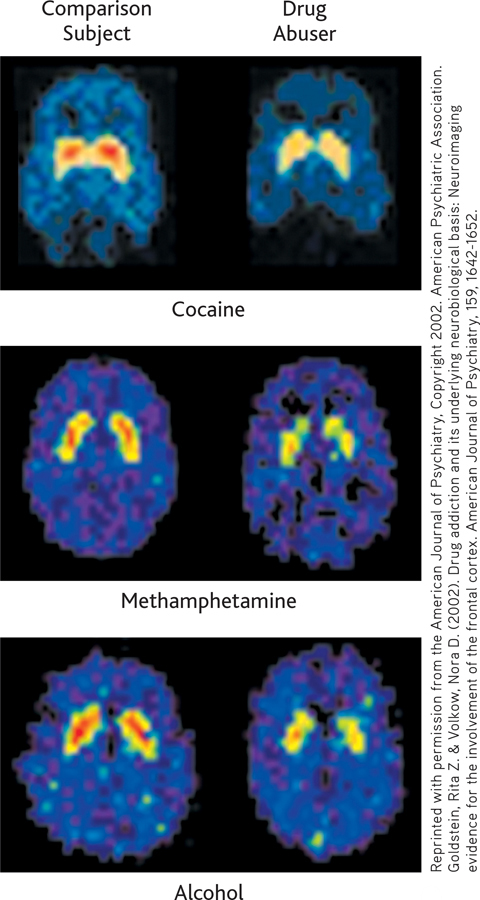
Common Effects of Addictive Drugs The intoxicating effects of all addictive drugs are produced by rapidly increasing dopamine levels in the brain’s reward system (Volkow & others, 2009, 2011b). As the brain adjusts to the effects of repeated drug use, long-term changes occur in the brain’s reward circuitry. The number of dopamine receptors is indicated by orange and yellow in the scans above. Substance abuse sharply reduces the number of dopamine receptors in the brain’s reward system.
Reprinted with permission from the American Journal of Psychiatry, Copyright 2002. American Psychiatric Association. Goldstein, Rita Z. & Volkow, Nora D. (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: Neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 1642-1652.