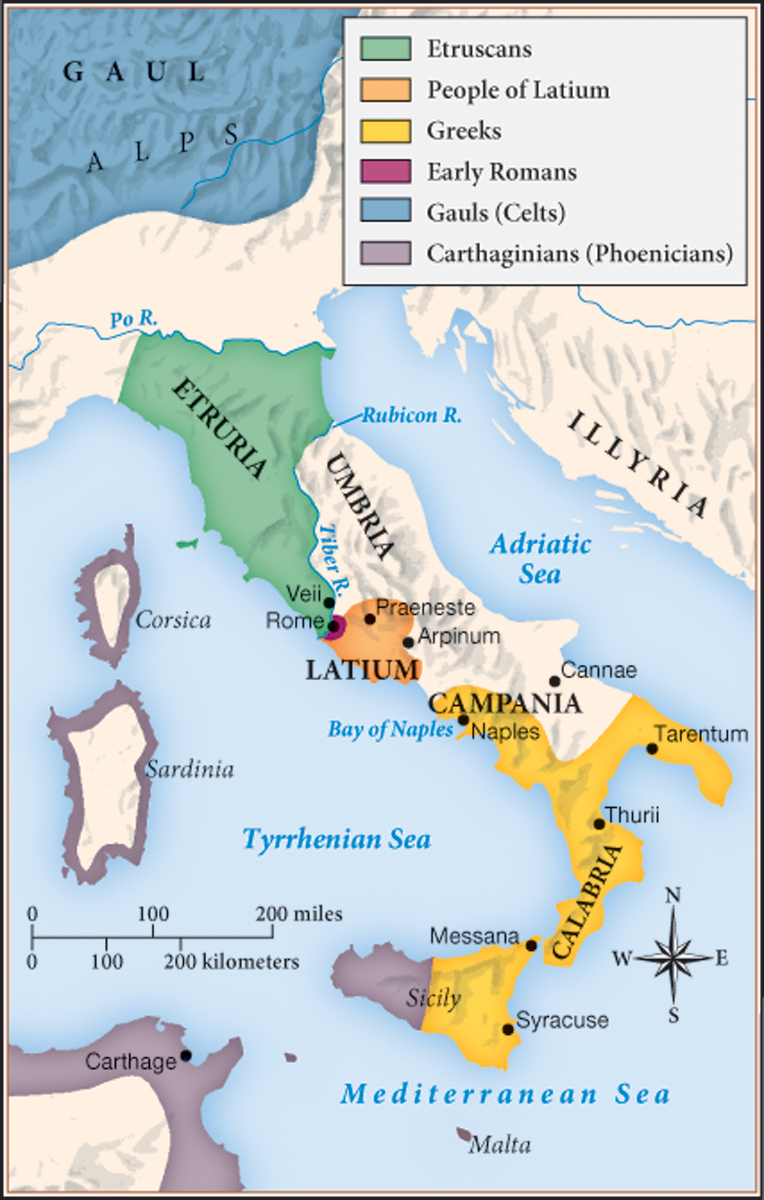
MAP 5.1 Ancient Italy, 500 B.C.E.
When the Romans overthrew the monarchy to found a republic in 509 B.C.E., they controlled a relatively small territory in central Italy. Many different peoples lived in Italy at this time, with the most prosperous occupying fertile agricultural land and sheltered harbors on the peninsula’s west side. The early republic’s most urbanized neighbors were the Etruscans to the north and the Greeks in the city-states to the south, including on the island of Sicily. Immediately adjacent to Rome were the people of Latium, called Latins. How did geography aid early Roman expansion in the Italian peninsula?