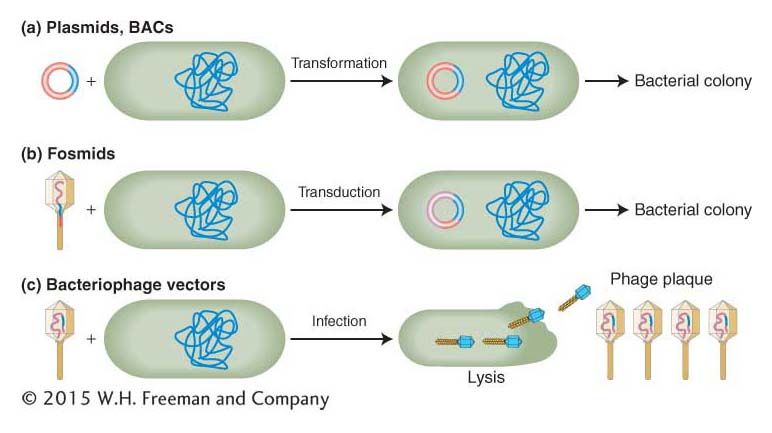
Recombinant DNA can be delivered into bacterial cells by transformation, transduction, or infection with a phage. (a) Plasmid and BAC vectors are delivered by DNA mediated transformation. (b) Certain vectors such as fosmids are delivered within bacteriophage heads (transduction); however, after having been injected into the bacterium, they form circles and replicate as large plasmids. (c) Bacteriophage vectors such as phage λ infect and lyse the bacterium, releasing a clone of progeny phages, all carrying the identical recombinant DNA molecule within the phage genome.