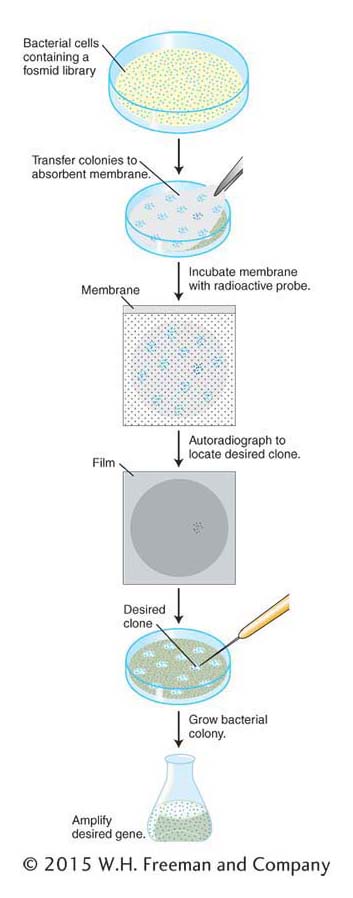
The clone carrying a gene of interest is identified by probing a genomic library, in this case made by cloning genes in a fosmid vector, with DNA or RNA known to be related to the desired gene. A radioactive probe hybridizes with any recombinant DNA incorporating a matching DNA sequence, and the position of the clone having the DNA is revealed by autoradiography. Now the desired clone can be selected from the corresponding spot on the petri dish and transferred to a fresh bacterial host so that a pure gene can be manufactured.