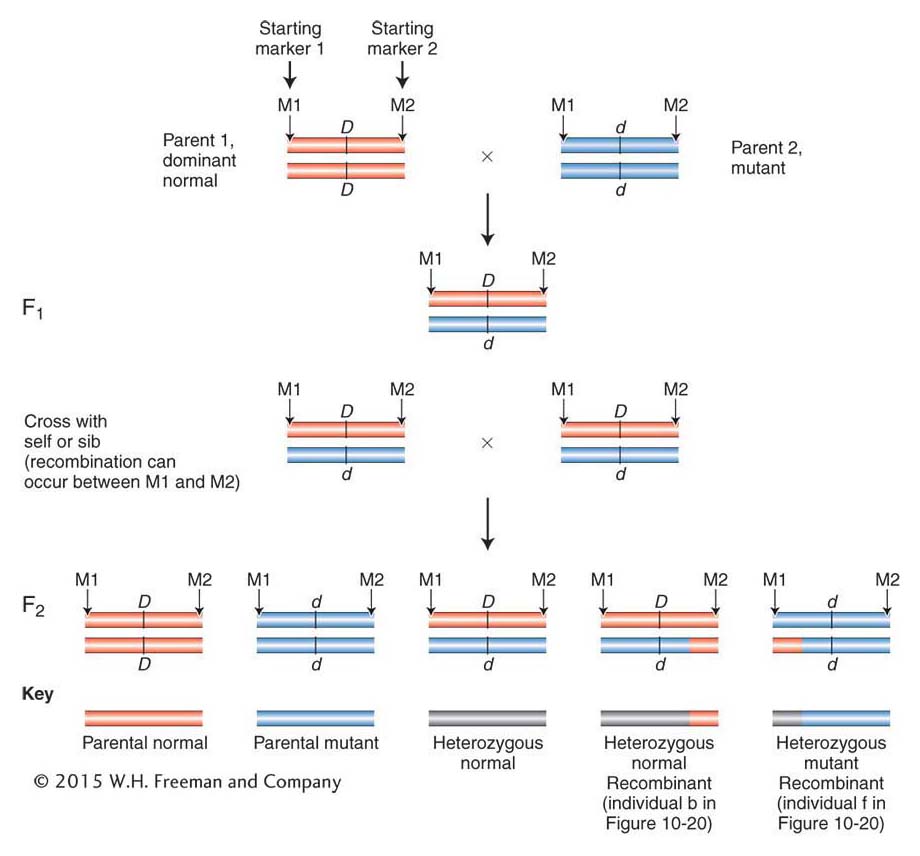
A modern gene hunt often begins with a cross between parents with contrasting traits. In the example shown, Parent 1 carries the wild-