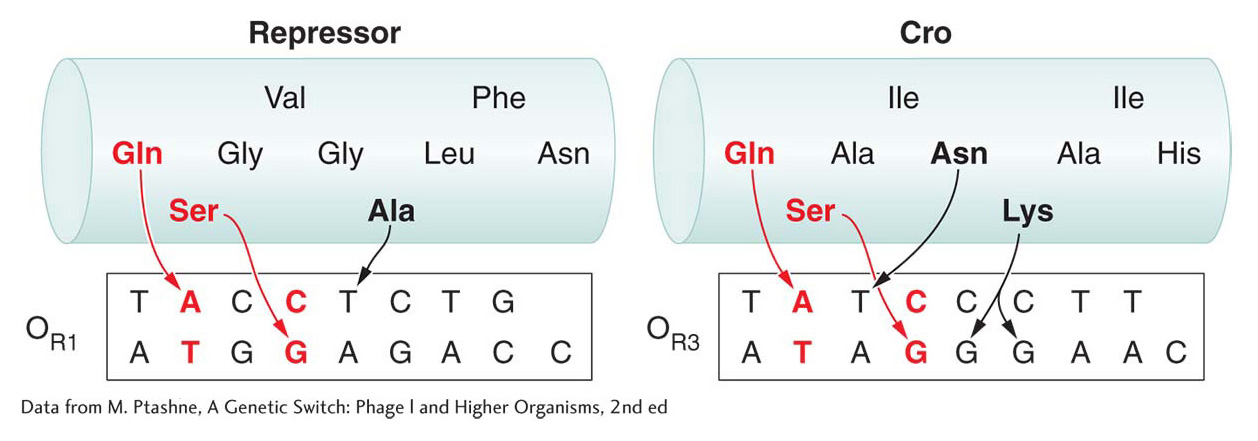
Interactions between amino acids and bases determine the specificity and affinity of DNA-
[Data from M. Ptashne, A Genetic Switch: Phage l and Higher Organisms, 2nd ed.]