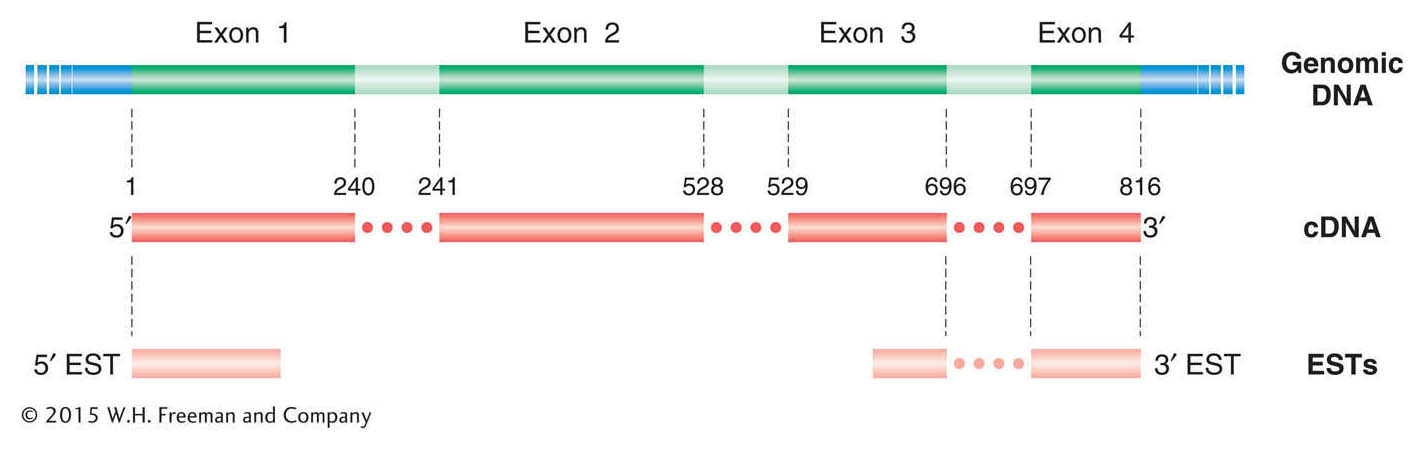
Alignment of fully sequenced complementary DNAs (cDNAs) and expressed sequence tags (ESTs) with genomic DNA. The dashed lines indicate regions of alignment; for the cDNA, these regions are the exons of the gene. The dots between segments of cDNA or ESTs indicate regions in the genomic DNA that do not align with cDNA or EST sequences; these regions are the locations of the introns. The numbers above the cDNA line indicate the base coordinates of the cDNA sequence, where base 1 is the 5′-most base and base 816 is the 3′-most base of the cDNA. For the ESTs, only a short sequence read is obtained from each end (5′and 3′) of the corresponding cDNA. These sequence reads establish the boundaries of the transcription unit, but they are not informative about the internal structure of the transcript unless the EST sequences cross an intron (as is true for the 3′ EST depicted here).