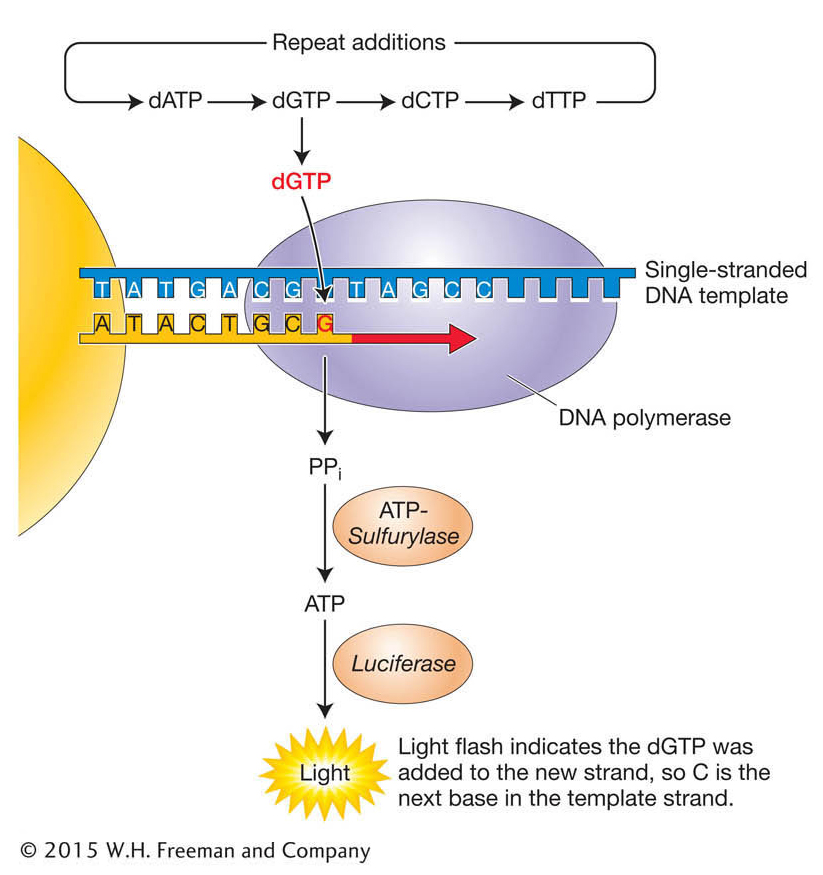
In the pyrosequencing process, nucleotides are sequentially added to form the complementary strand of the single- e-