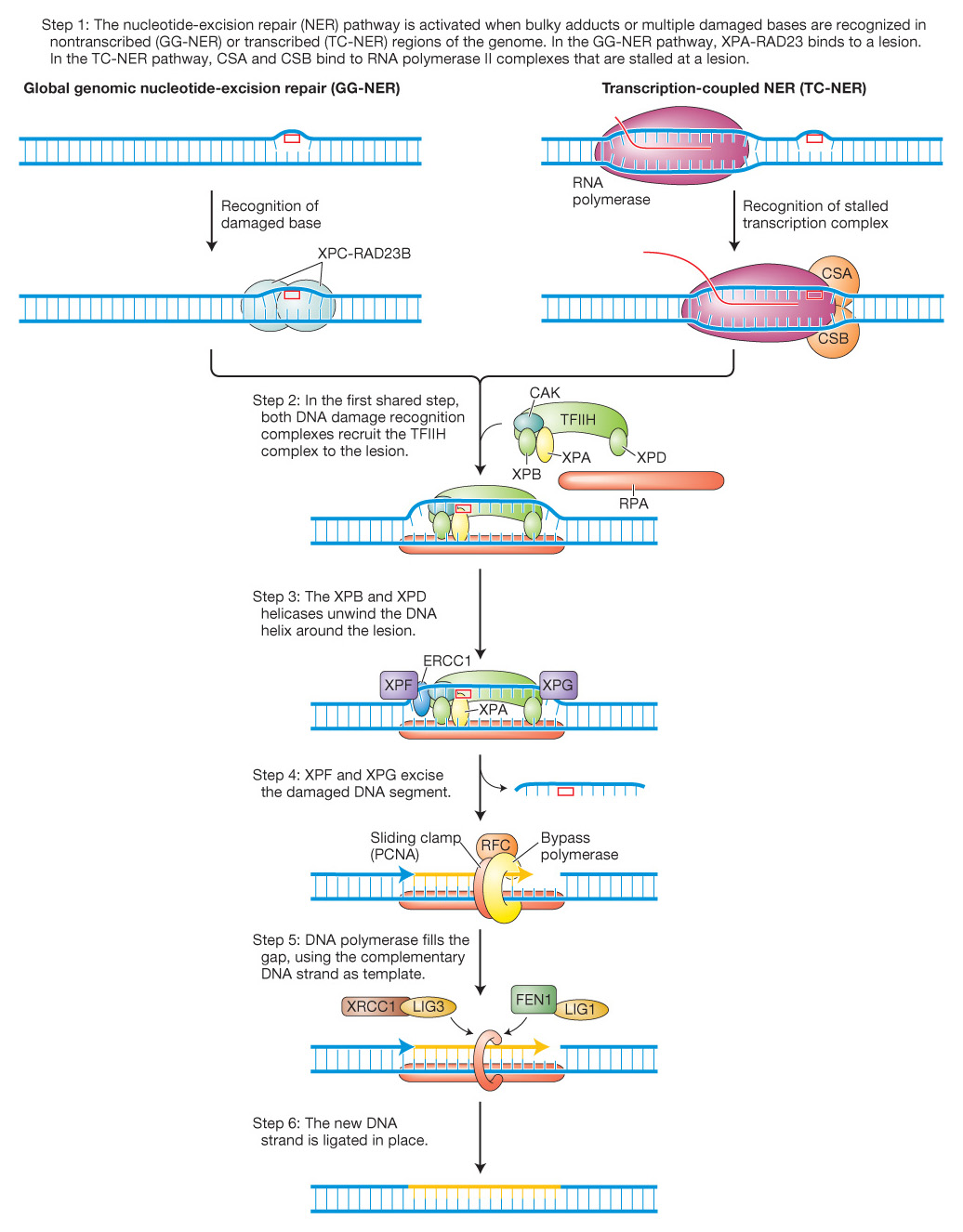
The nucleotide- G- C- 4-