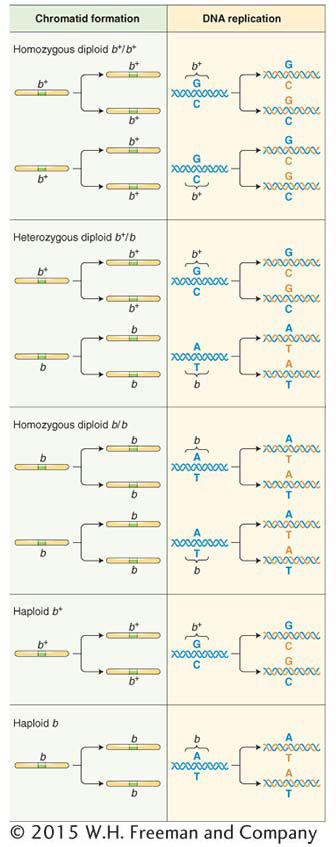
Each chromosome divides longitudinally into two chromatids (left); at the molecular level (right), the single DNA molecule of each chromosome replicates, producing two DNA molecules, one for each chromatid. Also shown are various combinations of a gene with wild-