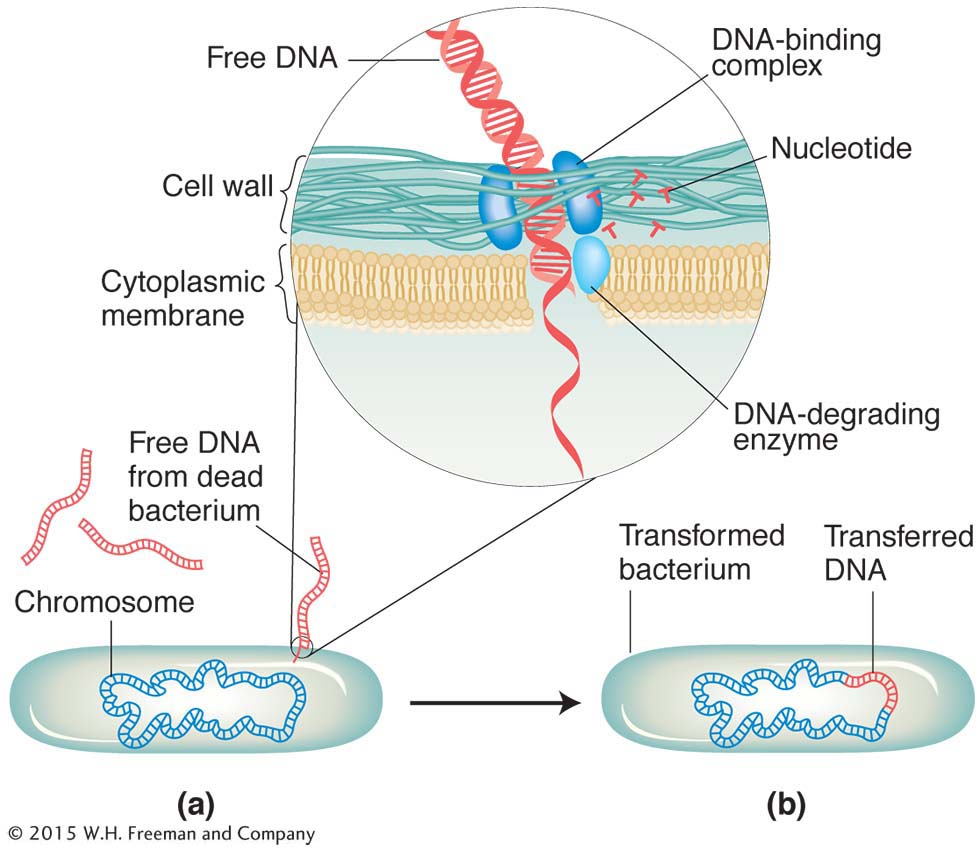
A bacterium undergoing transformation (a) picks up free DNA released from a dead bacterial cell. As DNA-