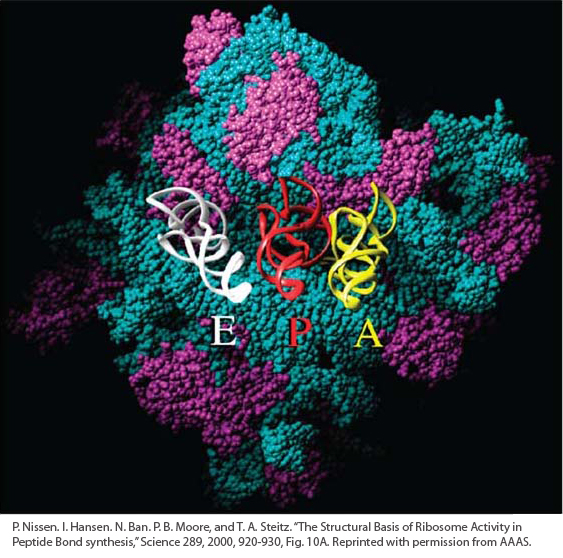
This image shows at atomic resolution a surface of the ribosome from the bacterium Haloarcula marismortui, deduced from X-
[P. Nissen, J. Hansen, N. Ban, P. B. Moore, and T. A. Steitz, “The Structural Basis of Ribosome Activity in Peptide Bond Synthesis,” Science 289, 2000, 920-