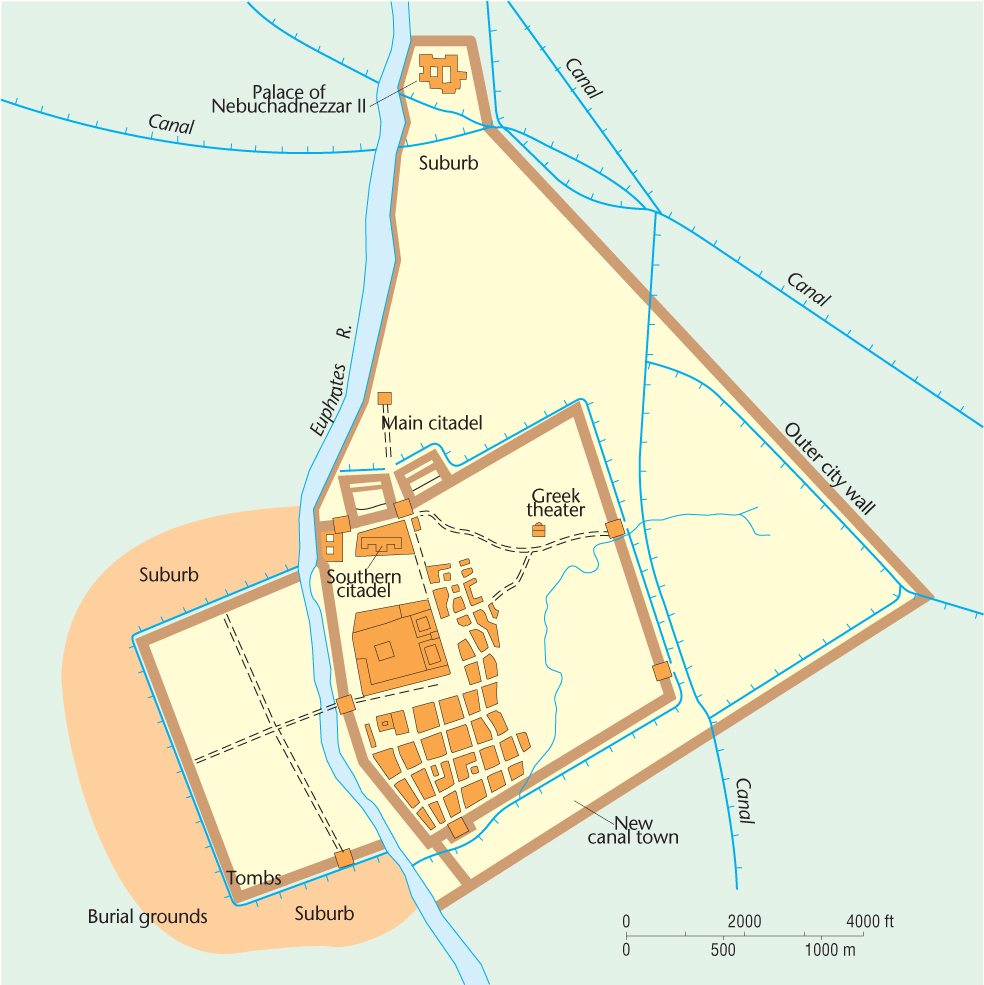
Figure 10.5: Map of Babylon illustrating the urban morphology of early Mesopotamian cities. The citadel in the inner city was characterized by the ziggurat, main temple, palace, or granary. Beyond the citadel lay the residential areas; we can assume they extended out to the inner walls and occupied both sides of the river. Suburbs grew outside the major gates and were occupied by people not allowed to spend the night in the city, such as traders and noncitizens.
(Source: After map in Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1984: 555.)