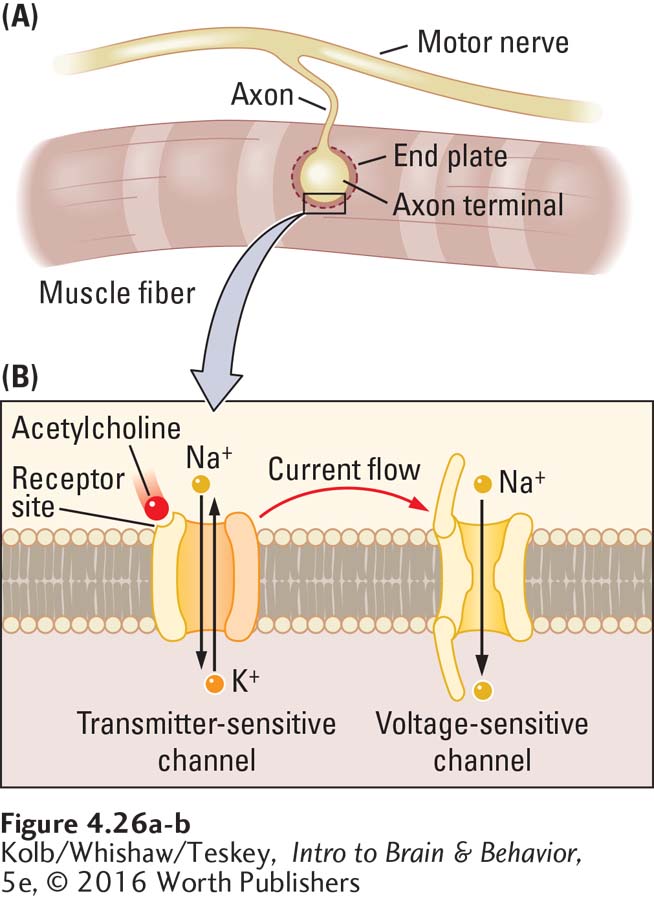
FIGURE 4- r- e-