PROBLEMS
Question 14.17
For each of the following transactions, what is the initial effect (increase or decrease) on M1? On M2?
You sell a few shares of stock and put the proceeds into your savings account.
You sell a few shares of stock and put the proceeds into your checking account.
You transfer money from your savings account to your checking account.
You discover $0.25 under the floor mat in your car and deposit it in your checking account.
You discover $0.25 under the floor mat in your car and deposit it in your savings account.
Question 14.18
There are three types of money: commodity money, commodity-
backed money, and fiat money. Which type of money is used in each of the following situations? Bottles of rum were used to pay for goods in colonial Australia.
Salt was used in many European countries as a medium of exchange.
For a brief time, Germany used paper money (the “Rye Mark”) that could be redeemed for a certain amount of rye, a type of grain.
The town of Ithaca, New York, prints its own currency, the Ithaca HOURS, which can be used to purchase local goods and services.
Question 14.19
The following table shows the components of M1 and M2 in billions of dollars for the month of December in the years 2003 to 2013 reported by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Complete the table by calculating M1, M2, currency in circulation as a percentage of M1, and currency in circulation as a percentage of M2. What trends or patterns about M1, M2, currency in circulation as a percentage of M1, and currency in circulation as a percentage of M2 do you see? What might account for these trends?
Year
Currency in circulation
Traveler’s checks
Checkable deposits
Savings deposits
Time deposits
Money market funds
M1
M2
Currency in circulation as a percentage of M1
Currency in circulation as a percentage of M2
2003
$662.5
$7.6
$635.9
$3,159.0
$818.1
$752.8
?
?
?
?
2004
697.8
7.5
670.6
3,506.5
828.4
677.6
?
?
?
?
2005
724.6
7.2
643.0
3,601.6
993.7
682.4
?
?
?
?
2006
750.2
6.7
610.6
3,691.8
1,206.0
776.6
?
?
?
?
2007
760.6
6.3
608.1
3,864.1
1,276.0
930.6
?
?
?
?
2008
816.2
5.5
782.0
4,085.6
1,457.6
1,021.6
?
?
?
?
2009
863.7
5.1
825.3
4,809.3
1,183.1
781.2
?
?
?
?
2010
918.7
4.7
912.7
5,329.6
927.9
675.7
?
?
?
?
2011
1,001.2
4.3
1,154.3
6,032.8
767.0
663.7
?
?
?
?
2012
1,090.0
3.8
1,353.5
6,687.5
633.0
642.0
?
?
?
?
2013
1,159.5
3.5
1,475.8
7,133.0
555.6
640.9
?
?
?
?
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Question 14.20
Indicate whether each of the following is part of M1, M2, or neither:
$95 on your campus meal card
$0.55 in the change cup of your car
$1,663 in your savings account
$459 in your checking account
100 shares of stock worth $4,000
A $1,000 line of credit on your Sears credit card
Question 14.21
Tracy Williams deposits $500 that was in her sock drawer into a checking account at the local bank.
How does the deposit initially change the T-
account of the local bank? How does it change the money supply? If the bank maintains a reserve ratio of 10%, how will it respond to the new deposit?
If every time the bank makes a loan, the loan results in a new checkable bank deposit in a different bank equal to the amount of the loan, by how much could the total money supply in the economy expand in response to Tracy’s initial cash deposit of $500?
If every time the bank makes a loan, the loan results in a new checkable bank deposit in a different bank equal to the amount of the loan and the bank maintains a reserve ratio of 5%, by how much could the money supply expand in response to Tracy’s initial cash deposit of $500?
Question 14.22
Ryan Cozzens withdraws $400 from his checking account at the local bank and keeps it in his wallet.
How will the withdrawal change the T-
account of the local bank and the money supply? If the bank maintains a reserve ratio of 10%, how will it respond to the withdrawal? Assume that the bank responds to insufficient reserves by reducing the amount of deposits it holds until its level of reserves satisfies its required reserve ratio. The bank reduces its deposits by calling in some of its loans, forcing borrowers to pay back these loans by taking cash from their checking deposits (at the same bank) to make repayment.
If every time the bank decreases its loans, checkable bank deposits fall by the amount of the loan, by how much will the money supply in the economy contract in response to Ryan’s withdrawal of $400?
If every time the bank decreases its loans, checkable bank deposits fall by the amount of the loan and the bank maintains a reserve ratio of 20%, by how much will the money supply contract in response to a withdrawal of $400?
Question 14.23
The government of Eastlandia uses measures of monetary aggregates similar to those used by the United States, and the central bank of Eastlandia imposes a required reserve ratio of 10%. Given the following information, answer the questions below.
Bank deposits at the central bank = $200 million
Currency held by public = $150 million
Currency in bank vaults = $100 million
Checkable bank deposits = $500 million
Traveler’s checks = $10 million
What is M1?
What is the monetary base?
Are the commercial banks holding excess reserves?
Can the commercial banks increase checkable bank deposits? If yes, by how much can checkable bank deposits increase?
Question 14.24
In Westlandia, the public holds 50% of M1 in the form of currency, and the required reserve ratio is 20%. Estimate how much the money supply will increase in response to a new cash deposit of $500 by completing the accompanying table. (Hint: The first row shows that the bank must hold $100 in minimum reserves—
20% of the $500 deposit— against this deposit, leaving $400 in excess reserves that can be loaned out. However, since the public wants to hold 50% of the loan in currency, only $400 × 0.5 = $200 of the loan will be deposited in round 2 from the loan granted in round 1.) How does your answer compare to an economy in which the total amount of the loan is deposited in the banking system and the public doesn’t hold any of the loan in currency? What does this imply about the relationship between the public’s desire for holding currency and the money multiplier? Round
Deposits
Required reserves
Excess reserves
Loans
Held as currency
1
$500.00
$100.00
$400.00
$400.00
$200.00
2
200.00
?
?
?
?
3
?
?
?
?
?
4
?
?
?
?
?
5
?
?
?
?
?
6
?
?
?
?
?
7
?
?
?
?
?
8
?
?
?
?
?
9
?
?
?
?
?
Total after 10 rounds
?
?
?
?
?
Question 14.25
What will happen to the money supply under the following circumstances in a checkable-
deposits- only system? The required reserve ratio is 25%, and a depositor withdraws $700 from his checkable bank deposit.
The required reserve ratio is 5%, and a depositor withdraws $700 from his checkable bank deposit.
The required reserve ratio is 20%, and a customer deposits $750 to her checkable bank deposit.
The required reserve ratio is 10%, and a customer deposits $600 to her checkable bank deposit.
Question 14.26
Although the U.S. Federal Reserve doesn’t use changes in reserve requirements to manage the money supply, the central bank of Albernia does. The commercial banks of Albernia have $100 million in reserves and $1,000 million in checkable deposits; the initial required reserve ratio is 10%. The commercial banks follow a policy of holding no excess reserves. The public holds no currency, only checkable deposits in the banking system.
How will the money supply change if the required reserve ratio falls to 5%?
How will the money supply change if the required reserve ratio rises to 25%?
Question 14.27
Using Figure 29-6, find the Federal Reserve district in which you live. Go to www.federalreserve.gov/
bios/ pres.htm and click on your district to identify the president of the Federal Reserve Bank in your district. Go to www.federalreserve.gov/ fomc/ and determine if the president of the regional Federal Reserve bank in your district is currently a voting member of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). Question 14.28
Show the changes to the T-
accounts for the Federal Reserve and for commercial banks when the Federal Reserve sells $30 million in U.S. Treasury bills. If the public holds a fixed amount of currency (so that all new loans create an equal amount of checkable bank deposits in the banking system) and the minimum reserve ratio is 5%, by how much will checkable bank deposits in the commercial banks change? By how much will the money supply change? Show the final changes to the T- account for the commercial banks when the money supply changes by this amount. Question 14.29
The Congressional Research Service estimates that at least $45 million of counterfeit U.S. $100 notes produced by the North Korean government are in circulation.
Why do U.S. taxpayers lose because of North Korea’s counterfeiting?
As of December 2014, the interest rate earned on one-
year U.S. Treasury bills was 0.13%. At a 0.13% rate of interest, what is the amount of money U.S. taxpayers are losing per year because of these $45 million in counterfeit notes?
Question 14.30
As shown in Figure 29-9, the portion of the Federal Reserve’s assets made up of U.S. Treasury bills has declined since 2007. Go to www.federalreserve.gov. Under “Select Statistical Releases,” click on “View All.” Under the heading “Money Stock and Reserve Balances,” click on “Factors Affecting Reserve Balances.” Click on the date of the current release.
Under “Statement of Condition of Federal Reserve Bank,” look in the “Total” column. What is the amount displayed next to “Total assets”? What is the amount displayed next to “U.S. Treasury securities”? What percentage of the Federal Reserve’s total assets are currently made up of U.S. Treasury bills?
Do the Federal Reserve’s assets consist primarily of U.S. Treasury securities, as they did in January 2007, the beginning of the graph in Figure 29-9, or does the Fed still own a large number of other assets, as it did in mid-
2013, the end of the graph in Figure 29-9?
Question 14.31
The accompanying figure shows new U.S. housing starts, in thousands of units per month, between January 1980 and January 2014. The graph shows a large drop in new housing starts in 1984–
1991 and 2006– 2009. New housing starts are related to the availability of mortgages. What caused the drop in new housing starts in 1984–
1991? What caused the drop in new housing starts in 2006–
2009? How could better regulation of financial institutions have prevented these two instances?
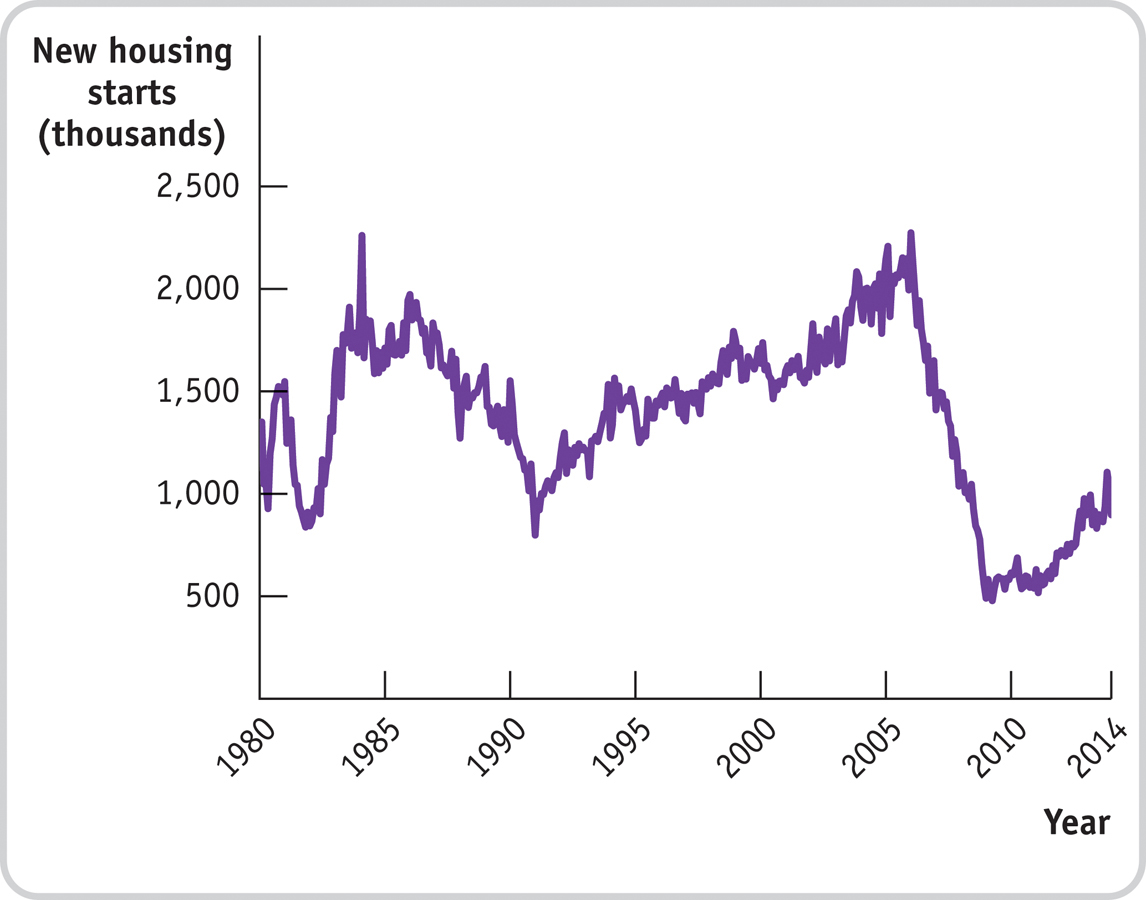 Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
WORK IT OUT
For interactive, step-
Question 14.32
16. Show the changes to the T-