FIGURE 19-3 Equilibrium in the Money Market
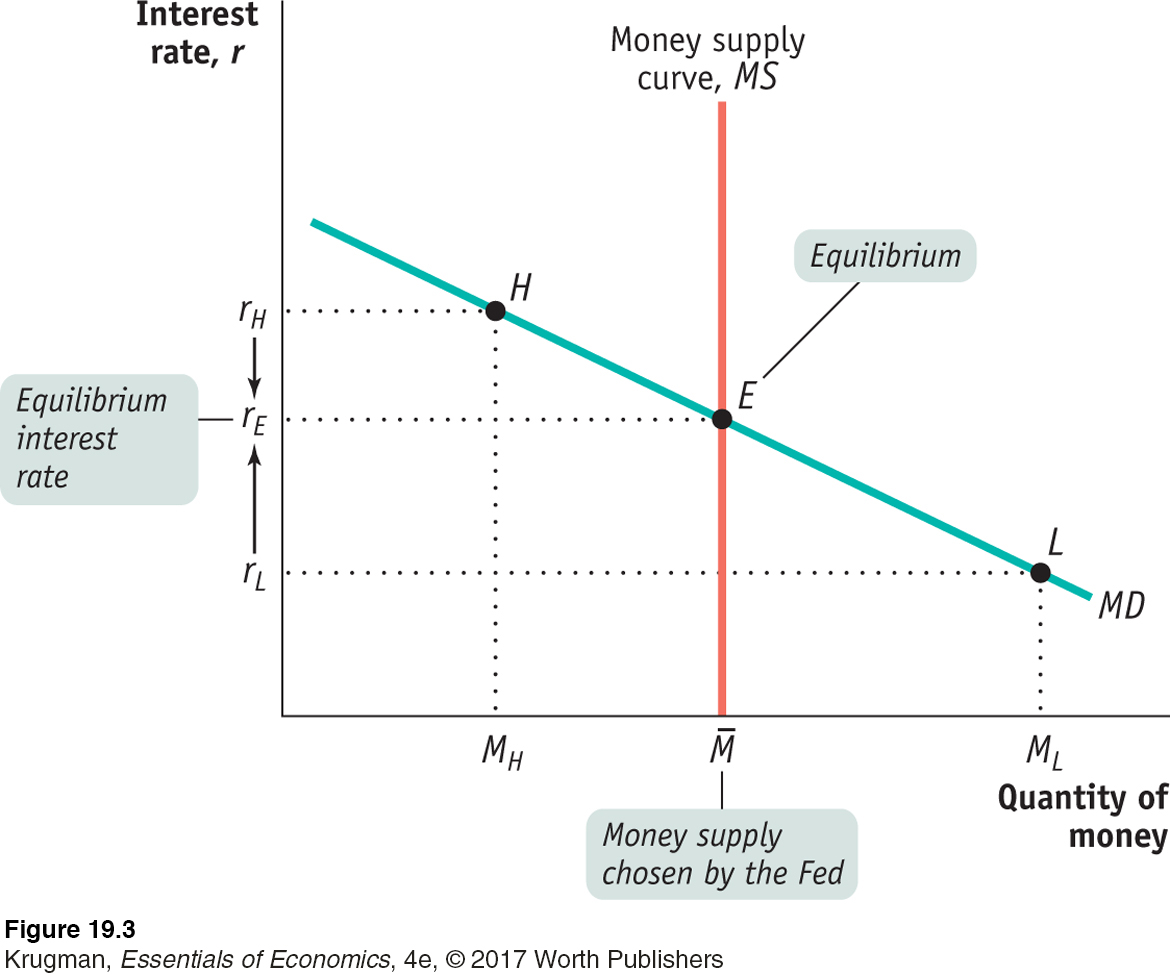 The money supply curve, MS, is vertical at the money supply chosen by the Federal Reserve, . The money market is in equilibrium at the interest rate rE: the quantity of money demanded by the public is equal to , the quantity of money supplied. At a point such as L, the interest rate, rL, is below rE and the corresponding quantity of money demanded, ML, exceeds the money supply, . In an attempt to shift their wealth out of nonmoney interest-bearing financial assets and raise their money holdings, investors drive the interest rate up to rE. At a point such as H, the interest rate rH exceeds rE and the corresponding quantity of money demanded, MH, is less than the money supply, . In an attempt to shift out of money holdings into nonmoney interest-bearing financial assets, investors drive the interest rate down to rE.
The money supply curve, MS, is vertical at the money supply chosen by the Federal Reserve, . The money market is in equilibrium at the interest rate rE: the quantity of money demanded by the public is equal to , the quantity of money supplied. At a point such as L, the interest rate, rL, is below rE and the corresponding quantity of money demanded, ML, exceeds the money supply, . In an attempt to shift their wealth out of nonmoney interest-bearing financial assets and raise their money holdings, investors drive the interest rate up to rE. At a point such as H, the interest rate rH exceeds rE and the corresponding quantity of money demanded, MH, is less than the money supply, . In an attempt to shift out of money holdings into nonmoney interest-bearing financial assets, investors drive the interest rate down to rE.

