100.8 Provides Instructors with These Resources
xii
FOR ASSESSMENT
Test Bank Fully revised for the Fourth Edition, the Test Bank contains multiple-
Graphing Questions Another question bank for instructors building assignments and tests. These are electronically gradable graphing questions that use our own graphing engine. Students are asked to draw graphs in response to a question; their graphs are automatically graded by the software.
End-
Graded Homework Assignments Each  unit concludes with a pre-
unit concludes with a pre-
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
A Gradebook This useful resource offers clear feedback to students and instructors on individual assignments and on performance in the course.
LMS integration Included so that  is easily integrated into a school’s learning management system and that an instructor’s Gradebook and roster are always in sync.
is easily integrated into a school’s learning management system and that an instructor’s Gradebook and roster are always in sync.
Instructor’s Resource Manual Offers instructors teaching materials and tips to enhance the classroom experience, along with chapter objectives, outlines, and other ideas.
Solutions Manual Prepared by the authors of the text, this manual offers detailed solutions to all of the text’s end-
Interactive Presentation Slides These brief, interactive, and visually interesting slides are designed to hold students’ attention in class. The slides include graphics and animations that demonstrate key concepts, real-
Also available for instructors and students, to be used with any text or homework system:
 FlipItEcon.com FlipIt gets students actively involved in learning economics in a fresh way. This resource was developed by two pioneers in active-
FlipItEcon.com FlipIt gets students actively involved in learning economics in a fresh way. This resource was developed by two pioneers in active-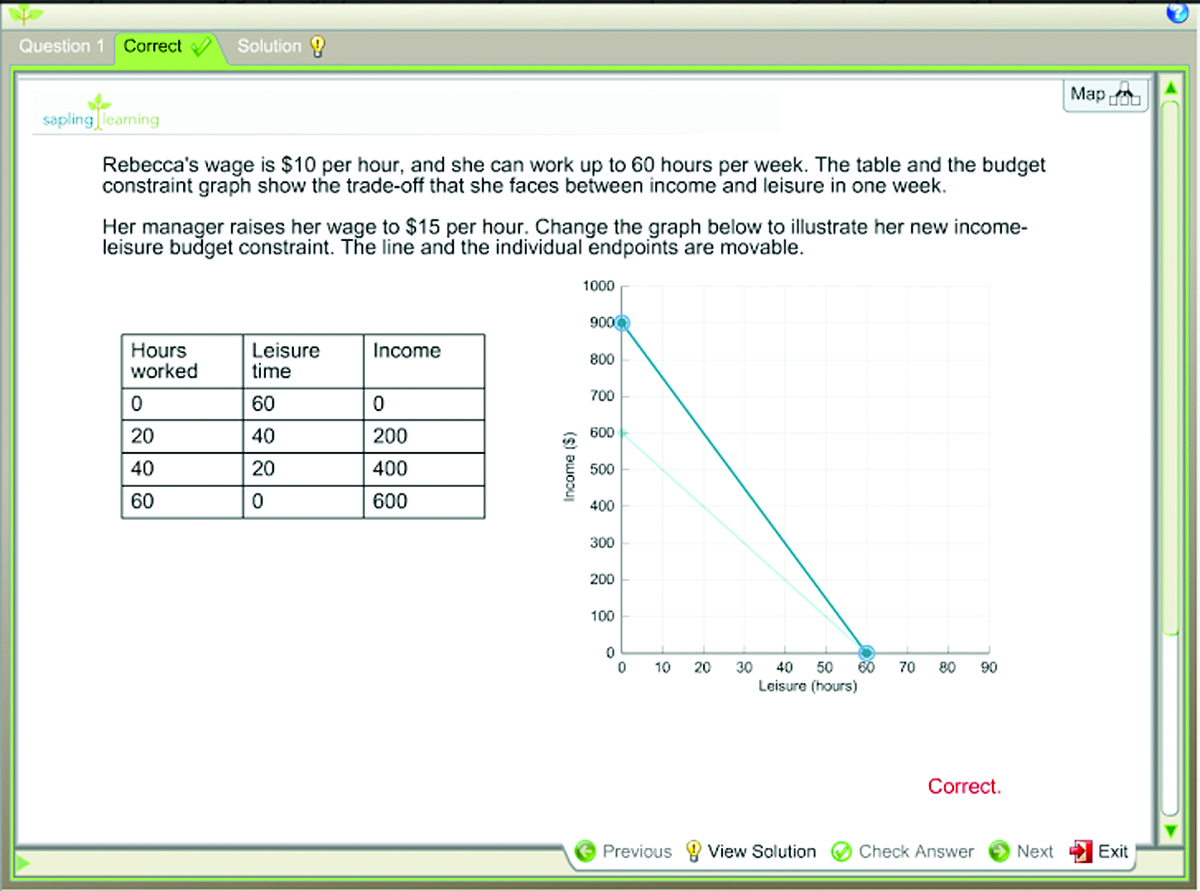
 Saplinglearning.com Sapling Learning is an online homework system that helps students get better grades with targeted instructional feedback tailored to each individual’s responses. It also helps instructors spend less time preparing for and managing a course by providing personalized classroom support from a PhD-
Saplinglearning.com Sapling Learning is an online homework system that helps students get better grades with targeted instructional feedback tailored to each individual’s responses. It also helps instructors spend less time preparing for and managing a course by providing personalized classroom support from a PhD-xiii
What’s New in This Edition?
| A New Chapter | Chapter 11, Poverty, Inequality, and the Welfare State |
| A New Feature | Work It Out problems in every chapter |
| 2 Major New Sections | Price Discrimination in Chapter 8, Monopoly |
| Game Theory in Chapter 9, Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition |
To teach students about the realities of resource scarcity and the need to make choices, we use fracking and its effects on the market for natural gas as the subject of the opening story for Chapter 3, on supply and demand.
In other cases we pay particular attention to how changes in technology are transforming the economic landscape—
Example topics illustrate important policy debates, such as the introduction of the Affordable Care Act and the environmental trade-
9 New Opening Stories
A Natural Gas Boom, 66
Deck the Halls, 202
The Coming of Obamacare, 315
The Pain in Spain*, 343
Hitting the Breaking Point, 377
Airpocalypse Now*, 407
Funny Money*, 506
The Most Powerful Person in Government, 541
The Everywhere Phone*, 569
10 New Business Cases
An Uber Way to Get a Ride, 172
Shopping Apps, Showrooming, and the Challenges Facing Brick-
Amazon and Hachette Go to War, 284
Hunting Endangered Animals to Save Them, 341
Welfare State Entrepreneurs*, 342
The Business Cycle and the Decline of Montgomery Ward, 404
Day Labor in the Information Age, 406
How Boeing Got Better, 473
Slow Steaming*, 474
Here Comes the Sun, 566
18 New Economics in Action Applications
Take the Keys, Please, 107
Price Controls in Venezuela*, 116
Crabbing, Quotas, and Saving Lives in Alaska, 128
Smart Grid Economics, 190
Farmers Move Up Their Supply Curves, 216
Why Is Your Broadband So Slow? And Why Does It Cost So Much?*, 249
How Much Does Your Electricity Really Cost?, 291
Long-
Programs and Poverty in the Great Recession, 327
What Medicaid Does, 334
French Family Values*, 337
Spain’s Costly Surplus*, 356
Is the End of Economic Growth in Sight?*, 418
Why Did Britain Fall Behind?*, 423
The Cost of Limiting Carbon*, 432
Austerity and the Multiplier, 486
Are We Greece?*, 498
How Hong Kong Lost Its Shirts*, 578
*indicates a global example.