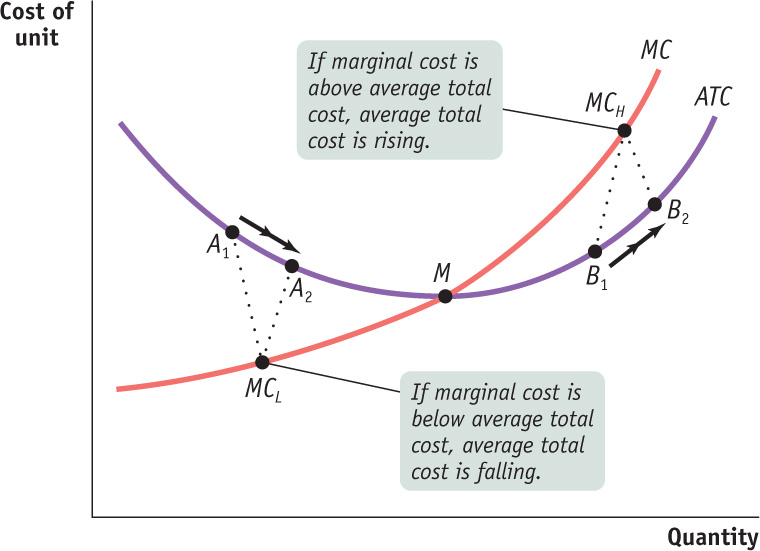
To see why the marginal cost curve (MC) must cut through the average total cost curve (ATC) at the minimum average total cost (point M), corresponding to the minimum-cost output, we look at what happens if marginal cost is different from average total cost. If marginal cost is less than average total cost (MCL), an increase in output must reduce average total cost, as in the movement from A1 to A2. If marginal cost is greater than average total cost (MCH), an increase in output must increase average total cost, as in the movement fromB1 to B2.